
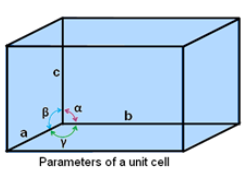
A unit cell is characterized by 6 parameters:
- 3-edges a, b and c (refer the diagram given above). The edges may or may not be perpendicular to each other.
- 3 angles α (between b and c), β(between a and c) and γ(between a and b).
Classification of unit cell:
Primitive Unit Cells:
When constituent particles are present only on the corner positions of a unit cell, it is called a primitive unit cell.
Centred Unit Cells:
When a unit cell contains one or more constituent particles present at positions other than corners in addition to those at corners, it is called a centred unit cell.
Centred unit cells are of three types:
Body-Centred Unit Cells:
Such a unit cell contains one constituent particle (atom, molecule or ion) at its body-centre besides the ones that are at its corners.
Face-Centred Unit Cells:
Such a unit cell contains one constituent particle present at the centre of each face, besides the ones that are at its corners.
End-Centred Unit Cells:
In such a unit cell, one constituent particle is present at the centre of any two opposite faces besides the ones present at its corners.

