Abnormal Molar Masses
In some cases, observed colligative properties deviate from their normal calculated values due to association or dissociation of molecules. As we know,
Colligative property α 1/ MB
Higher and lower values of molar mass are observed in case of association and dissociation respectively, e.g., in benzene, acetic acid gets associated, so, its observed molecular mass is 120. Similarly, KCI under undergoes dissociation in aqueous solution, so its observed molecular mass is 37.25.
These observed values are corrected by multiplying with Van’t Hoff factor (i).
Van’t Hoff Factor (i)
It is the ratio of the observed value of the colligative property to the calculated value of the colligative property.

So to correct the observed value of molar mass, van’t Hoff factor (i) must be included in the differential expression for colligative properties.

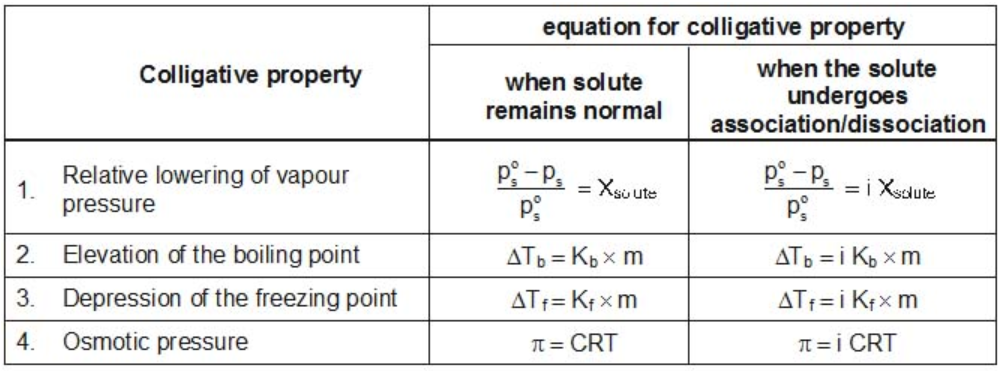
Modified Equations for Colligative Properties
For solutes which undergo dissociation or association in solutions, the equations for the colligative properties are modified by inserting the Van’t-Hoff’s factor in them as follows: