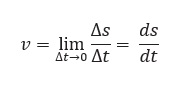The time rate of change of position of the object in any direction is called the speed of the object.
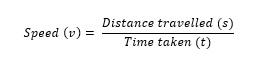
Its unit is m/s. It is a scalar quantity.
Its dimensional formula is [M0 T-1].
Uniform Speed:
If an object covers equal distances in equal intervals of time, then its speed is called uniform speed.
Non-Uniform Speed or Variable Speed:
If an object covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time, then its speed is called non-uniform or variable speed.
Average Speed:
The ratio of the total distance traveled by the object to the total time taken is called the average speed of the object.
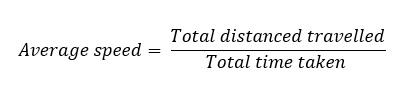
If a particle travels distances s1 , s2 , s3 …sn with speeds v1 , v2 , v3 …vn then
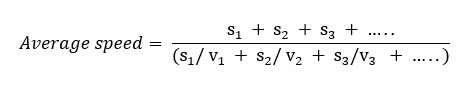
If particle travels equal distances ( s1 = s2 = s) with velocities v1 and v2 , then
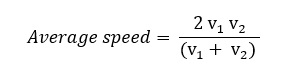
If a particle travels with speeds v1, v2, v3 …vn, during time intervals t1, t2, t3 …tn then
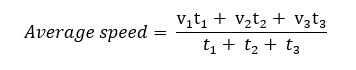
If particle travels with speeds v1 and v2 for equal time intervals, i.e., t1 =t2, =t3 then
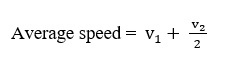
When a body travels equal distance with speeds v1 and v2 the average speed (v) is the
harmonic mean of two speeds.
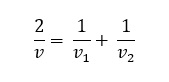
Instantaneous Speed:
When an object is traveling at a variable speed, then its speed at a given instant of time is called its instantaneous speed.