
What is Chemical kinetics?
Chemical kinetics is the branch of chemistry which deals with the study of rates (or fastness) of chemical reactions, the factors affecting it and the mechanism by which the reactions proceed.
Rate of Reaction
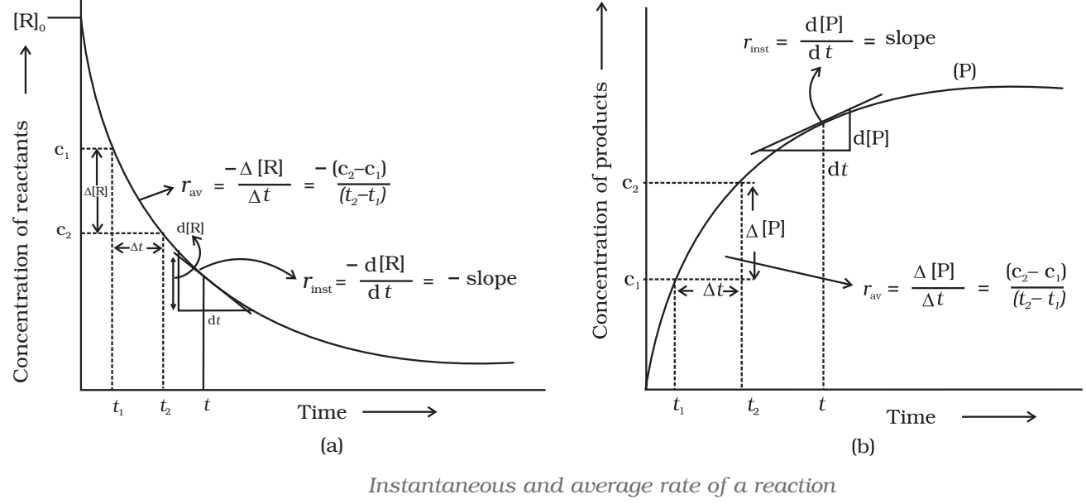
The rate of a reaction can be defined as the change in concentration of a reactant or product in unit time.
Let a reaction whose volume remains constant RP
One mole of reactant R produces one mole of product P. [R1] & [P1] and [R2] & [P2] the concentrations of R & P at time t1 and t2 respectively.
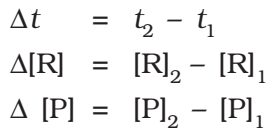
Where,
The square brackets in the above expressions are used to express molar concentration.


Both above expressions show the average rate of reaction
The rate measured over a long-time interval called average rate
![]()
Units of the rate of reaction:
- Concentration → time-1
- Mol → L-1s-1
Instantaneous rate of reaction
It is the rate of change of concentration (i.e. change of concentration per unit time) of any one of the reactants or products at that particular instant of time.
![]()
The overall rate of reaction explains:
When there are several reactants and products the individual rates of the various components may differ as they would depend on the stoichiometric coefficients.
For a reaction,
A + 2B → 3C +4D
The rate of disappearance of B = 2 × Rate of disappearance of A (2:1)
The rate of formation of C = 3 × Rate of disappearance of A (3:1)
The rate of formation of D = 4 × Rate of disappearance of A (4:1)
To define a unique value for the overall rate of the reaction we divide the individual rates by the respective coefficients and equate their signs.
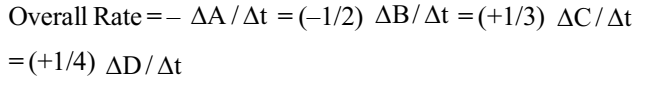
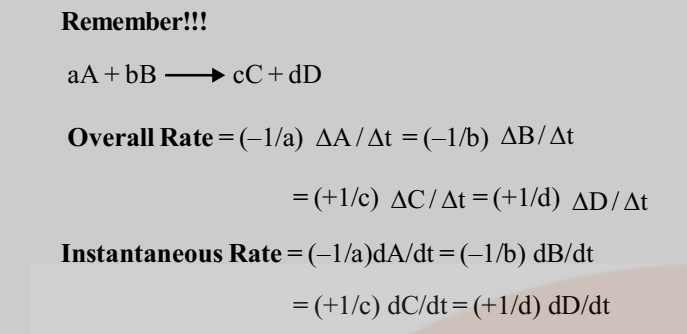
Factors affecting the Rate of reaction
- Concentration: As the concentration of reactant increase, the rate of reaction also increases.
- Temperature: Rate of reaction increases with the increase of temperature mostly reaction rate double with the rise of 100 temperature.
- Catalyst: Catalyst generally increase the rate of the reaction without undergoing in the reaction, it also help in attaining the equilibrium quickly without disturbing the equilibrium state in the reversible reaction.

