
Diazonium Salts
![]()
Structure of Diazonium Salt
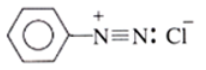
Preparation of Diazonium Salt

The reaction of preparation of diazonium salt is called Diazotization.
Physical Properties of Diazonium Salt
- It is a colourless crystalline solid.
- It is readily soluble in water and is stable in cold but reacts with water when warmed.
- It has tendency to explode when dry.
Chemical Reactions of Diazonium Salts
There are two types of reactions given by benzene diazonium chloride:
- Substitution reactions involving replacement of diazonium group.
- Coupling reactions involving the retention of diazo group acts as an electrophile.
Explanation:
- Substitution reactions involving replacement of diazonium group:
- Replacement by halide or cyanide ion:

Above reaction taking place in the presence of Cu(I) ion is called Sandmeyer reaction.
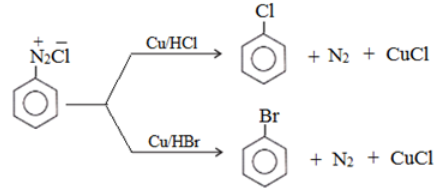
Above reaction taking place in the presence of copper powder is named as the Gatterman reaction.
Replacement by iodide ion:

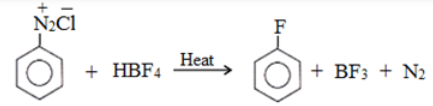
Replacement by fluoride ion:
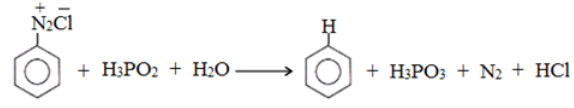
Replacement by H-atom:

Replacement by hydroxyl group:
Replacement by –NO2 group:

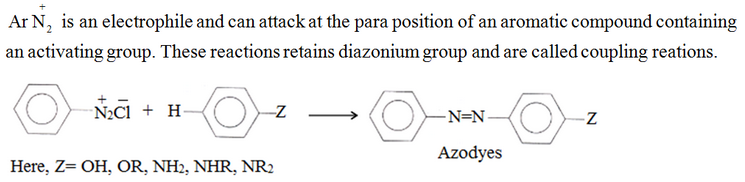
Reactions involving retention of diazo group
Coupling reactions:
Uses of Amine
- The most important amine is aniline which is used in the synthesis of medicines, dyes, etc
- N, N – Dmethylaniline (DMA) also used in the preparation of Methyl orange and other dyes
- Amines are widely used in developing chemicals for crop protection and water purification
- 1, 6 – Hexamethylenediamine H2N ‒ (CH2)6 ‒ NH2 is used in the production of nylon
- Adrenaline is an amine hormone that prepares the human beings for emergency situation
- Amino acids form the building blocks of proteins in human beings

