The magnetic field lines are a visual and intuitive realization of the magnetic field. Electric field lines of an electric dipole are also displayed in Fig.(c). Their properties are:
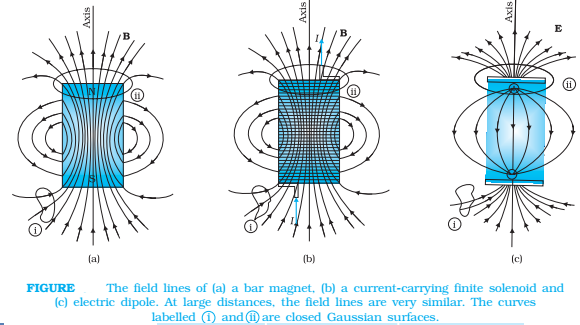
- The magnetic field lines of a magnet (or a solenoid) form continuous closed loops. This is unlike the electric dipole where these field lines begin from a positive charge and end on the negative charge or escape to infinity.
- The tangent to the field line at a given point represents the direction of the net magnetic field B at that point.
- The larger the number of field lines crossing per unit area, the stronger is the magnitude of the magnetic field B. In Fig.(a), B is larger around region ii than in region i.
- The magnetic field lines do not intersect, for if they did, the direction of the magnetic field would not be unique at the point of intersection.

