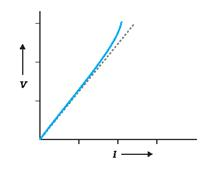
The electric current I flowing through a substance is proportional to the voltage V across its ends, i.e.,
V ∝ I
V = RI,
where R is called the resistance of the substance.
The unit of resistance is ohm: 1Ω = 1 V A-1.
The resistance R not only depends on the material of the conductor but also on the dimensions of the conductor.
Important Points related to Ohm’s Law:
Ohm’s Law,

Unit: Current I in ampere (A) , potential difference V is in volt (V)
Resistance of a uniform conductor,
![]()
Unit: ohm (Ω)
Resistivity or specific resistance,

Unit: Ωm
Conductance,

Unit: ohm-1 or mho or Siemens(S)
Conductivity = 1/Resistivity
Unit: Ω-1m-1
Current density = Current/Area
Unit: Am-2

