
Oxygen is the first element of Group 16 with the electronic configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p4 in the ground state. Oxygen has two allotropes: dioxygen(O2) and trioxygen or ozone (O3).
Dioxygen (O2)
Oxygen usually exists in the form of dioxygen.
Preparation of Oxygen (O2):
Dioxygen is prepared in the laboratory by thermal decompositions of oxygen-rich compounds such as KClO3,
![]()
It is also prepared by the hydrolysis of sodium peroxide.
![]()
Electrolysis of water also produces dioxygen in the pure state.
![]()
Properties of Oxygen (O2):
- Oxygen is a colourless, odourless and is a highly reactive tasteless gas.
- Due to the presence of pπ‒ pπ bonding, O2 is a discrete molecule and intermolecular forces are weak van der Waals forces, hence, O2 is a gas.
- Dioxygen combines with metals and non-metals to form binary compounds called oxides.
Examples are:

Some compounds are catalytically oxidized.
For example:

Uses of Oxygen:
- Dioxygen is used in making steel.
- It is used in the production of oxygen-containing organic chemicals.
- Dioxygen is also used for sewage treatment, river revival and paper pulp bleaching.
- It is used as an oxidizer in underwater diving and in space shuttles.
For getting IT professional certificate online ExamSnap CompTIA provides a lots for IT certificate online.
Simple Oxides
Oxygen combines with the majority of the elements of the periodic table to forms oxides (O2‒). There are three types of oxides:
- Acidic oxides: Oxides of non- metals are usually acidic in nature. For example, SO2 combines with water to give H2SO3, an acid.
![]()
- Basic oxides: Metallic oxides are mostly basic in nature. Basic oxides dissolve in water to give a basic solution. For example, CaO combines with water to give Ca(OH)2, a base.
![]()
- Amphoteric oxides: Some metallic oxides show characteristics of both acidic as well as basic oxides. Such oxides are known as amphoteric oxides. For example, Al2O3 reacts with acids as well as alkalies.
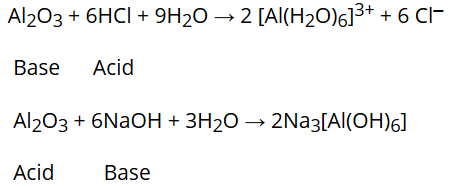
Ozone (O3)
Ozone is an allotropic form of oxygen. Ozone has an angular structure with a bond angle of about 117o. Both O = O bonds are of equal bond length due to resonance.

Preparation of Ozone:
It is formed when dioxygen is irradiated with UV light or silent electric discharge.
![]()
Properties of Ozone:
- Ozone is a pale blue gas with a characteristic pungent odour.
- Ozone is diamagnetic in nature.
- It is the second most powerful oxidising agent after fluorine. It liberates oxygen gas when acting as an oxidising agent.
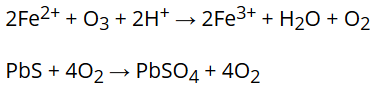
Depletion of ozone layer:
Thinning of the ozone layer is termed as depletion of ozone layer. The depletion of ozone layer in the stratosphere is caused by the presence of chlorofluorocarbons. CFCs decomposed by UV radiation to produce chlorine which reacts with ozone and this causes a decrease in the concentration of ozone at a rate faster than its formation from dioxygen. Another cause of depletion of ozone layer is the release of nitrogen oxides into the stratosphere by supersonic jet aeroplanes.

