A scalar quantity is a quantity with magnitude only. It is specified completely by a single number, along with the proper unit.
Examples are: the distance between two points, mass of an object, the temperature of a body
The rules for combining scalars are the rules of ordinary algebra. Scalars can be added, subtracted, multiplied and divided just as the ordinary numbers.
Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar:
When a vector A is multiplied by a scalar S, then its magnitude becomes S times, and unit is the product of units of A and S but direction remains same as that of vector A.
Scalar or Dot Product of Two Vectors:
The scalar product of two vectors is equal to the product of their magnitudes and the cosine of the smaller angle between them. It is denoted by . (dot).
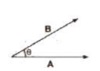
A * B = AB cos θ
The scalar or dot product of two vectors is a scalar.
Properties of Scalar Product
- Scalar product is commutative, i.e., A * B= B * A
- Scalar product is distributive, i.e., A * (B + C) = A * B + A * C
- The scalar product of two perpendicular vectors is zero.
A * B = AB cos 90° = O - Scalar product of two parallel vectors is equal to the product of their magnitudes, i.e., A *
B = AB cos 0° = AB - Scalar product of a vector with itself is equal to the square of its magnitude, i.e.,
A * A = AA cos 0° = A2 - Scalar product of orthogonal unit vectors.

