Almost all solids, liquids and gases expand on heating. The increase in the size of a body when it is heated is called thermal expansion.
Different type of thermal expansion:
Linear expansion:
It is the increase in the length of a metal rod on heating.
Superficial expansion:
It is the increase in the surface area of a metal sheet on heating.
Cubical expansion:
It is the increase in the volume of a block on heating.
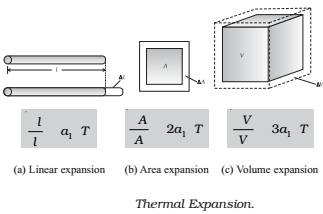
If the substance is in the form of a long rod, then for a small change in temperature, ΔT, the fractional change in length, ∆l/l, is directly proportional to ΔT.
![]()
where α1 is known as the coefficient of linear expansion.
Similarly, we consider the fractional change in volume, ∆V/V, of a substance for temperature change ∆T and define the coefficient of volume expansion, αV as
![]()
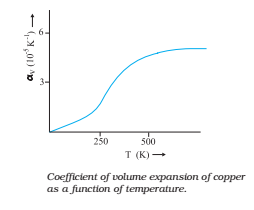
Here αV is also a characteristic of the substance but is not strictly a constant. It depends in general on temperature (Fig). It is seen that αV becomes constant only at a high temperature.

