
In an AC circuit, the current and emf vary continuously with time. Therefore power at a given instant of time is calculated and then its mean is taken over a complete cycle. Thus, we define the instantaneous power of an a.c. circuit as the product of the instantaneous emf and the instantaneous current flowing through it.
The instantaneous value of emf and current is given by
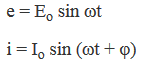
where φ is the phase difference between the emf and current in an a.c circuit
The average power consumed over one complete cycle is
![]()
where ϕ is the phase difference between the emf and current in an a.c. circuit.
The average power consumed over and complete cycle
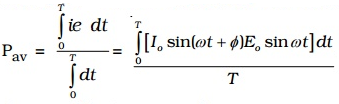
On simplification, we obtain
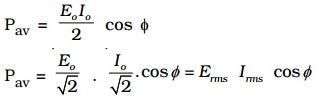
Pav = apparent power × power factor
where Apparent power = Erms Irms and power factor = cos ϕ
Power factor:
The average power of an a.c. circuit is given by
![]()
The product Erms ,Irms does not give the actual power and is called apparent power. It gives actual or true power only when multiplied by factor cosϕ. The factor cosϕ is called the power factor of an a.c. circuit.
The average power of an ac circuit is also called the true power of the circuit.
True power = apparent power × power factor
For a pure inductive or capacitive circuit, ϕ = 900.
∴ Power factor = cos 900 = 0.
Thus the power factor assumes the minimum value for a purely inductive or capacitive circuit.
For a pure resistive circuit, ϕ = 00.
∴ Power factor = cos 00 = 1.
Thus the power factor assumes the maximum value for a purely resistive circuit.

