
Modulation is the process of variation of some characteristics of a carrier wave in accordance with the instantaneous value of a modulating signal.
Types of modulations:
- Amplitude modulation
- Frequency modulation
- Phase modulation
- Pulse modulation
Need for modulation: It is due to the fact that low-frequency signal
- needs antenna of very large length (≈ 5 km):
For transmitting a signal, we need an antenna or an aerial. This antenna should have a size comparable to the wavelength of the signal (at least λ/4 in dimension) so that the antenna properly senses the time variation of the signal.
- mixes up of the signal transmitted from different stations:
There is a need for translating the original low-frequency baseband message or information signal into high-frequency wave before transmission such that the translated signal continues to possess the information contained in the original signal. In doing so, we take the help of a high-frequency signal, known as the carrier wave, and a process known as modulation which attaches information to it. The carrier wave may be continuous (sinusoidal) or in the form of pulses as shown in Fig.
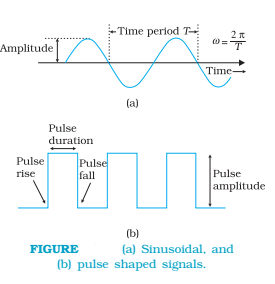
A sinusoidal carrier wave can be represented as
![]()
- get attenuated significantly. As power radiated by antenna is given by
![]()
This implies that for the same antenna length, the power radiated increases with decreasing λ, i.e., increasing frequency. Hence, the effective power radiated by a long wavelength baseband signal would be small. For a good transmission, we need high powers and hence this also points out to the need of using
high-frequency transmission.

