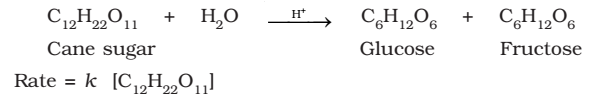
Half-Life of a Reaction
The half-life of a reaction is the time in which the concentration of a reactant is reduced to one half of its initial concentration.
Represented as: t1/2
- For a zero order reaction, rate constant is given by equation.
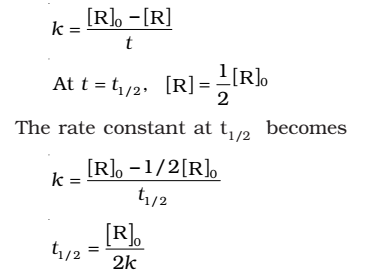
- For the first order reaction,
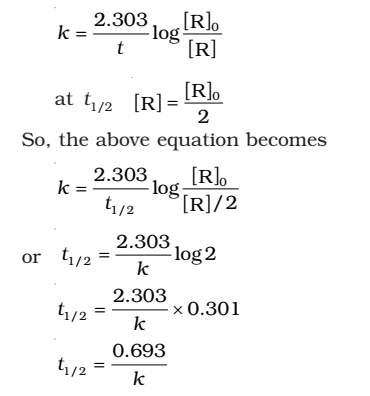
Pseudo First-Order Reactions
Reactions which are not truly of the first order but under certain conditions become reactions of the first order.
Example:
![]()
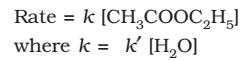
The concentration of water does not get altered much during the course of the reaction. So, in the rate equation the term [H2O] can be taken as constant.
![]()