
Effect of Catalyst on Rate of Reaction
A catalyst is a substance which alters the rate of a reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change.
Example:
![]()
The action of the catalyst
According to intermediate complex theory, reactants first combine with catalyst to form intermediate complex which then decomposes to form the products and regenerating the catalyst.
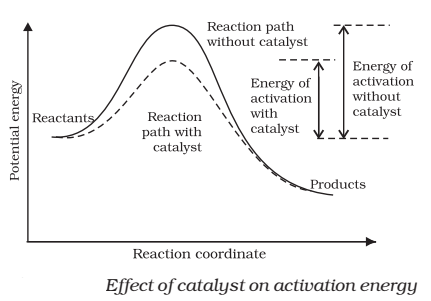
Catalyst provides an alternate pathway by reducing the activation energy between reactants and products and hence lowering the potential energy barrier.
Important characteristics of catalyst:
- A small amount of the catalyst can catalyze a large amount of reactants.
- A catalyst does not alter Gibbs energy, G of a reaction.
- It catalysis the spontaneous reactions but does not catalyze non-spontaneous reactions.
- A catalyst does not change the equilibrium constant of a reaction rather, it helps in attaining the equilibrium faster.

