Biomolecules
Biomolecules are the organic molecules that are involved in the maintenance and metabolic processes of living organisms. Thus, they build up the living system and are responsible for their growth and maintenance.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones or the compounds which upon hydrolysis produce polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones.
- They are optically active due to the presence of chiral ‘C’.
- They are also called saccharides (From Latin word Saccharum = sugar) due to sweet taste.
Classification of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are classified on the basis of their behaviour on hydrolysis. They have been broadly divided into following three groups.
Monosaccharides:
These are the carbohydrates which cannot get hydrolyzed into simpler molecules. For example glucose, fructose, galactose etc.
Disaccharides:
These are the carbohydrates that yield two to ten monosaccharide units, on hydrolysis. For example: sucrose, lactose, maltose.
Polysaccharides:
These are the high molecular mass carbohydrates which on hydrolysis yield a large number of monosaccharides. For example: starch, cellulose, glycogen, gums, etc.
Note: Monosaccharides and oligosaccharides are crystalline solids, soluble in water and sweet in taste. These are known as Sugars. Polysaccharides are amorphous, insoluble in water and tasteless. There are called Non-sugars.
Reducing sugars:
These are the carbohydrates which contain free aldehydic or ketonic group and reduces Fehling’s solution or Tollen’s reagent. For example: Maltose, lactose.
Non Reducing Sugars:
These are the carbohydrates which do not contain free functional group and do not reduce Fehling’s or Tollen’s reagent. For example: Sucrose.
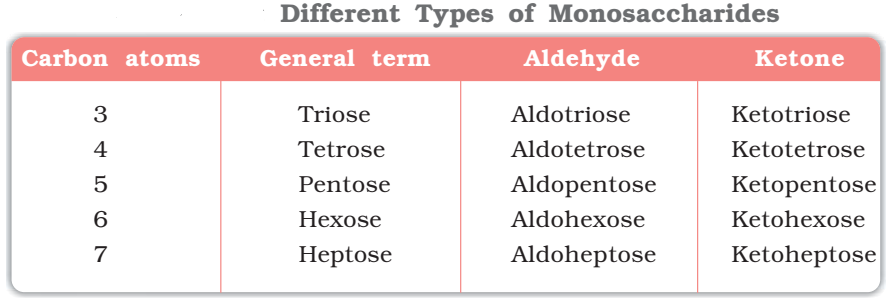
Monosaccharides
A carbohydrate that cannot be hydrolysed further to give simpler units of polyhydroxy aldehyde or ketone is called a monosaccharide. Some common examples are glucose, fructose, ribose, etc.
Monosaccharides are further classified on the basis of number of carbon atoms and the functional group present in them. If a monosaccharide contains an aldehyde group, it is known as an aldose and if it contains a keto group, it is known as a ketose.