Progressive Wave:
A wave that travels from one point of the medium to another is called a progressive wave. A progressive wave may be transverse or longitudinal.
Plane progressive harmonic wave:
If during the propagation of a wave through a medium, the particles of the medium vibrate simply harmonically about their mean positions, then the wave is said to be a plane progressive harmonic wave.
Displacement relation for a progressive harmonic wave:
The displacement in a sinusoidal wave propagating in the positive x-direction is given by
![]()

where a is the amplitude of the wave, k is the angular wave number, ω is the angular frequency, (kx – ωt + φ) is the phase, and φ is the phase constant or phase angle.
The sine function and the time-dependent phase of a wave correspond to the oscillation of a string element, and the amplitude of the wave determines the extremes of the element’s displacement. The constant ϕ is called the initial phase angle.
Wavelength
Wavelength λ of a progressive wave is the distance between two consecutive points of the same phase at a given time. In a stationary wave, it is twice the distance between two consecutive nodes or antinodes. k is called the propagation constant or the angular wave number.
Its SI unit is radian per meter or rad m-1.
Period and Frequency:
Period T of oscillation of a wave is defined as the time any element of the medium takes to move through one complete oscillation. It is related to the angular frequency ω through the relation
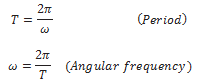
Frequency v of a wave is defined as 1/T and is related to angular frequency by
![]()
It is the number of oscillations per unit time made by a string element as the wave passes through it. It is usually measured in Hertz.

