
Electrochemical cell and Gibbs Energy of the Reaction
Electrical work done in one second is equal to electrical potential multiplied by total charge passed. If we want to obtain maximum work from a galvanic cell then charge has to be passed reversibly. The reversible work done by a galvanic cell is equal to decrease in its Gibbs energy and therefore if the emf of the cell is E and nF is the amount of charge passed and ΔrG is the Gibbs energy of the reaction, then
![]()
It may be remembered that E(cell) is an intensive parameter but ΔrG is an extensive thermodynamic property and the value depends on n. Thus, if we write the reaction
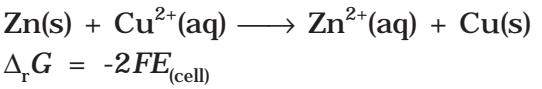
But when we write the reaction
![]()
![]()
If the concentration of all the reacting species is unity, then E(cell)
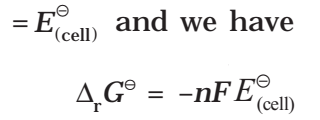
Thus, from the measurement of E–Cell we can obtain an important thermodynamic quantity, ΔrG–, standard Gibbs energy of the reaction.
From the latter we can calculate equilibrium constant by the equation:
![]()

