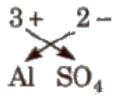Ionic or Electrovalent Bond
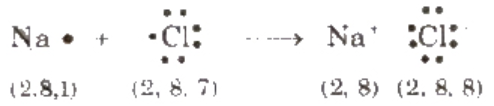
A chemical bond formed by complete transference of elements from one atom (metal) to another (non-metal) and hence, each atom acquires the stable nearest noble gas configuration, is called ionic bond or electrovalent bond, e.g., formation of sodium chloride.
Favourable factors for the formation of ionic bonds
- Metal should have lowest ionization enthalpy.
- Non-metal must have highest electron gain enthalpy.
- The energy released during the formation of 1 mole of crystal lattice, i.e., lattice enthalpy must be high.
[Some elements exhibit variable electrovalency. The reason for this is the unstable configuration of penultimate orbit and inert effect].
Ions
Species carrying either positive or negative charge are termed as ions. Species carrying positive charge are called cations and that carrying negative charge are called anions. Metals usually form cation while non-metals (except H) usually form anions.
General Characteristics of Ionic Compounds
- Ionic compounds are usually solids in nature.
- Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points.
- Ionic compounds are soluble in polar solvents like water but insoluble in non-polar solvents like benzene, etc.
- Ionic compounds are good conductor in molten state and in aqueous solution.
- Ionic compounds have crystal structure.
Method of writing Formula of Ionic Compound
- Write the symbol of cation at the left and anion at the right.
- Write their electrovalence in figures on the top of each symbol as AXBY.
- Divide their valencies by HCF.
- Now apply cross-cross rule as
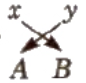
i.e., the formula is AyBx.
e.g., the formula of aluminium sulphate is Al2(So4)3.