For objects in uniformly accelerated rectilinear motion, the five quantities, displacement x, the time took t, initial velocity v0, final velocity v and acceleration a are related by a set of simple equations called kinematic equations of motion :
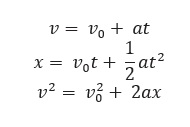
if the position of the object at time t = 0 is 0. If the particle starts at x = x0 , x in above equations is replaced by (x- x0).
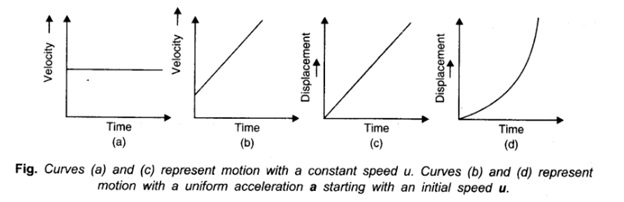
Kinematical Graphs
The ‘displacement-time’ and the ‘velocity-time’ graphs of a particle are often used to provide us with a visual representation of the motion of a particle. The ‘shape’ of the graphs depends on the initial ‘co-ordinates’ and the ‘nature’ of the acceleration of the particle (Fig.)
Equations of Uniformly Accelerated Motion
If a body starts with velocity (u) and after time t its velocity changes to v, if the uniform acceleration is a and the distance traveled in time t in s, then the following relations are obtained, which are called equations of uniformly accelerated motion.
- v = u + at
- s = ut + at2
- v2 = u2 + 2as
Distance traveled in nth second

If a body moves with uniform acceleration and velocity changes from u to v in a time interval, then the velocity at the midpoint of its path
√u2 + v2/ 2
Motion under Gravity
If an object is falling freely (u = 0) under gravity, then equations of motion
- v = u + gt
- h =ut +gt2
- v2 = u2 + 2gh
Note: If an object is thrown upward then g is replaced by – g in above three equations. It thus follows that
Time is taken to reach maximum height:
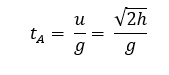 Maximum height reached by the body:
Maximum height reached by the body:
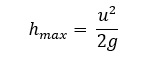
A ball is dropped from a building of height h and it reaches after t seconds on earth. From the same building if two balls are thrown (one upwards and other downwards) with the same velocity u and they reach the earth surface after t, and t2 seconds respectively, then
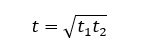
When a body is dropped freely from the top of the tower and another body is projected horizontally from the same point, both will reach the ground at the same time.


Thank you for providing this comprehensive overview of kinematic equations and motion principles. It’s a helpful reference for understanding the basics of uniformly accelerated motion and gravity-related calculations.