
Mirror:
A smooth and highly polished reflecting surface is called a mirror.
Plane Mirror
A highly polished plane surface is called a plane mirror.
Different properties of image formed by plane mirror
- Size of image = Size of object
- Magnification == Unity
- Distance of image == Distance of object
- A plane mirror may form a virtual as well as real image.
- A man may see his full image in a mirror of half height of man.
When two plane mirror are held at an angle θ, the number of images of an object placed between them is given as below:
- n = [(360° / θ) – 1 ], where 360° / θ is an integer.
- n = integral part of 360° / θ, when 360° is not an integer.
[A plane mirror may form a real image when the pencil of light incident on the mirror is convergent. Children, during their play form an image of sun as wall by a strip of plane mirror.]
- If keeping an object fixed a plane mirror is rotated in its plane by an angle θ, then the reflected ray rotates in the same direction by an angle 2 θ.
- Focal length, as well as radius of curvature of a plane mirror, is infinity. Power of a plane mirror is zero.
- An image formed by a plane mirror is virtual, erect, laterally inverted, of same size as that of object and at the same distance as the object from the mirror.
Spherical Mirror
A highly polished curved surface whose reflecting surface is a cut part of hollows at glass sphere is called a spherical mirror. Spherical mirrors are of two types:
Concave Mirror
A spherical mirror, whose bent in surface is reflecting surface, is called a concave mirror.
Convex Mirror:
A spherical mirror, whose bulging out surface is reflecting surface, is called a convex mirror.
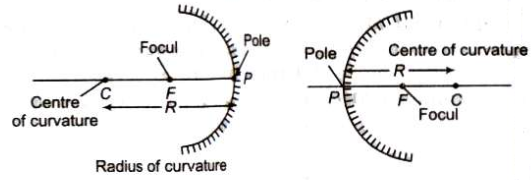
Some Terms Related to Spherical Mirrors are given below:
- Centre of Curvature: It is the centre of the sphere of which the mirror or lens is a part.
- Radius of Curvature (R): The radius of the hollow sphere of which the mirror is a part, is called radius of curvature.
- Pole: The central point of the spherical mirror is called its pole (P).
- Focus: When a parallel beam of light rays is incident on a spherical mirror, then after reflection it meets or appears to meet at a point on principal axis, which is called focus of the spherical mirror.
- Focal Length: The distance between the pole and focus is called focal length (f). Relation between focal length and radius of curvature is given by f=R/2
The power of a mirror is given as P = 1/f (meter) - Mirror formula: 1/f = 1/v + 1/u
where f = focal length of the mirror, u = distance of the object and v = distance of the image.
Newton’s formula for a concave mirror
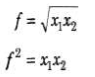
where x1 and x2 are the distances of object and image from the focus.

