
Phosphorus forms two types of halides, PX3 (X = F, Cl, Br, I) and PX5 (X = F, Cl, Br).
- Phosphorus trichloride, PCl3
- Phosphorus pentachloride, PCl5
| Phosphine, PH3 | Phosphorus Trichloride, PCl3 | Phosphorus pentachloride, PCl5 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explain | Phosphine is a highly poisonous, colourless gas and has a smell of rotten fish. | This is a type of halides. It is a colourless oily liquid. |
It is molecular in gas and liquid phase, but in solid state exists as [PCl4]+ PCl6]– containing tetra and hexa-coordinated phosphorous species.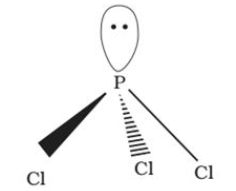 |
| Preparation | Phosphine is prepared by the reaction of calcium phosphide with water or dilute HCl. |
It is obtained by passing dry chlorine over heated white phosphorus or by the action of thionyl chloride with white phosphorus.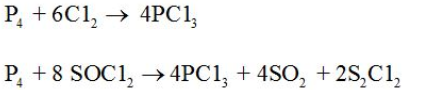 |
Phosphorus pentachloride is prepared by the reaction of white phosphorus with excess of dry chlorine or can be prepared by the action of SO2Cl2 on phosphorus.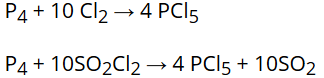 |
| Properties | It is insoluble in water and is a weaker base than ammonia. Like ammonia, it gives phosphonium compounds with acids. For example: In water, PH3 decomposes in the presence of light to give red phosphorus and H2. |
It has a pyramidal shape, in which phosphorus is sp3 hybridised. It gets hydrolysed in the presence of moisture. |
In gaseous and liquid phases, its has a trigonal bipyramidal structure.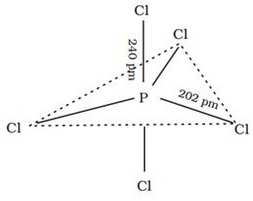 PCl5 is a yellowish white powder and in moist air, it hydrolyses to POCl3 and finally gets converted to phosphoric acid. PCl5 is a yellowish white powder and in moist air, it hydrolyses to POCl3 and finally gets converted to phosphoric acid. When heated, it sublimes but decomposes on stronger heating. When heated, it sublimes but decomposes on stronger heating.
|
Comparison between Phosphine and Ammonia
| Property | Phosphine | Ammonia |
|---|---|---|
| Colour | Colourless | Colourless |
| Decomposition by electric spark | Decomposes into elements | Decomposes into elements |
| Action with chlorine | Reacts violently to form PCl5 | Reacts with chlorine to form nitrogen trichloride |
| Action with halogen acids | Forms phosphonium salts | Forms ammonium salts |
| Combustibility | Burns in air to form phosphoric acid | Burns in air to form nitrogen and water. |
| Smell | Unpleasant smell of rotten fish. | Characteristic ammoniacal smell. |
| Density | Heavier than air | Lighter than air |
| Solubility | Sparingly soluble in water | Highly soluble in water |
| Nature | Highly poisonous | Non- poisonous |
| Action towards | Neutral | Basic |
| Stability | Less stable | More stable |
| Stability of salts | Less | More |

