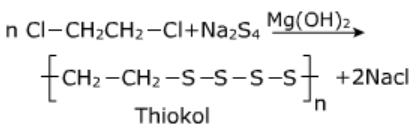Type of Rubbers:
Natural rubber:
Natural rubber has remarkable elasticity and it undergoes long-range reversible extensions.
- It is manufactured from latex-latex is obtained from bark trees.
Structure: Chemically natural rubber is a linear 1,4-addition polymer of isoprene (2-methyl-1, 3-Butadiene)

Vulcanized Rubber:
Natural rubber is very soft and brisk. It has high water absorption capacity and low tensile strength.
- Its properties can be improved by a process called vulcanization. It is consisting of heating raw rubber with Sulphur at 373-415 k to increase the rate of reaction zinc oxide is added.
- During vulcanization Sulphur bridges are or cross-links between polymer chains are introduced either at their reactive allylic position or at double bond site.
- Thus, due to vulcanization rubber becomes hard and stronger and remove tackiness of natural rubber.

Synthetic rubbers:
These may be defined as vulcanizable rubber like polymers which is capable of getting stretched twice to its length.
- Neoprene: It is polymer of chloroprene (2-chloro, -1,3-butatiene)
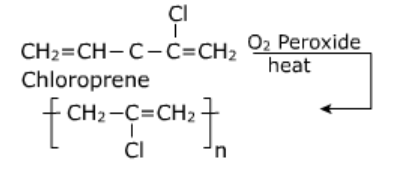
Uses:
- It is used in the manufacture of noses, gaskets.
- It is used as an insulator and for making conveyor belts and printing rollers.
Buna-N:
It is a rubber obtained by copolymerization of 1,3-butadiene and acrylonitrile in presence of peroxide catalyst.
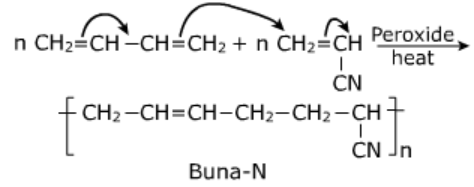
Uses:
- It is resistant to the action of petrol, lubricating oils and organic solvents, it is used for making oil seals, hoses and tank linings.
Thiokol:
It is prepared by copolymerization of 1,2-dichloroethane with sodium tetra sulphide [Na2SO4] in presence of Mg(OH)2