
The stability of the coordination compound depends on
Nature of the ligand:
Chelating ligands form strong and more stable complexes than the monodentate ligands. The π- bond ligands forms more stable complexes than the σ- bonded complex.
Nature of the metal atom/ion:
Small, highly charged metal ions form more stable complexes than large size, lowly charged metal ion.
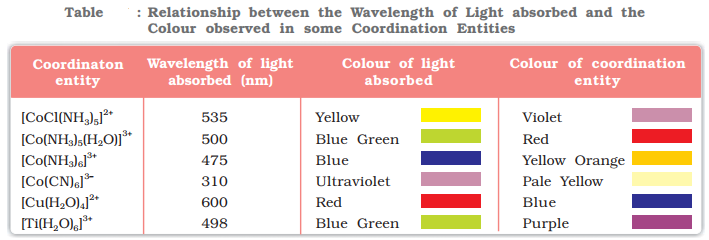
Color in Coordination Compounds
- The crystal field theory attributes the colour of the coordination compounds to d-d transition of the electron, i.e., the transiton of electron from t2g level to the higher eg level which accompanies the absorption of light in visible spectrum.
- In the absence of ligands, crystal field splitting does not occur and hence the substance is colourless.
Limitations of crystal field theory
- It does not take into account the partly covalent character of bonding between the ligand and the central atom.
- It is also unable to explain the relative strengths of ligands e.g., it does not explain why H2O is stronger ligand than OH−.

