Disaccharides:
The two monosaccharides are joined together by an oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule. Such a linkage between two monosaccharide units through oxygen atom is called glycosidic linkage.
Sucrose
It is one of the common disaccharides, which on hydrolysis gives equimolar mixture of D (+) -glucose and D (−) fructose.
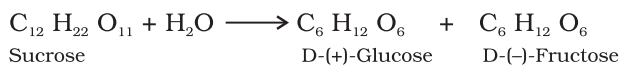
For example: In sucrose, the glycosidic linkage is present between glucose and fructose.

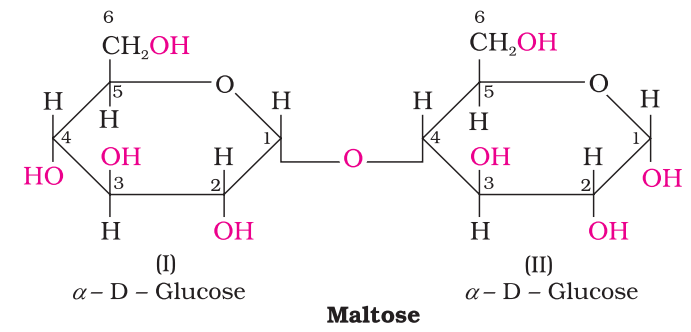
Maltose
Another disaccharide, maltose is composed of two α-D-glucose units in which C1 of one glucose (I) is linked to C4 of another glucose unit (II). The free aldehyde group can be produced at C1 of second glucose in solution and it shows reducing properties so it is a reducing sugar.
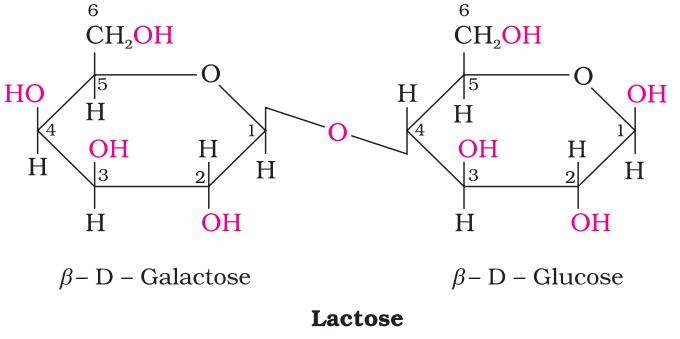
Lactose
It is more commonly known as milk sugar since this disaccharide is found in milk. It is composed of β-D-galactose and β-D-glucose. The linkage is between C1 of galactose and C4 of glucose. Hence it is also a reducing sugar.