
Asexual Reproduction
The mode depends on the body design of the organism.
Fission
The parent cell divides/splits into two daughter cell-Binary Fission; splits into many cells-multiple Fission.
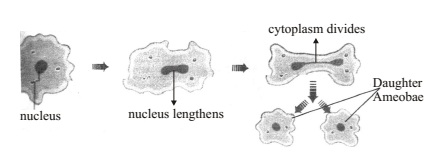
The process where nucleus lengthens is NUCLEOKINESIS and where the cytoplasm lenghthens is CYTOKINESIS.
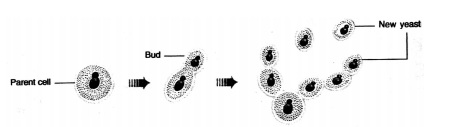
Budding
A bud develops as an outgrowth on parent body due to repeated cell division at a specific site. These buds detach from the parent body when they mature. E.g. Hydra, yeast.
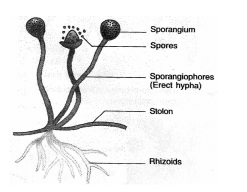
Spore Formation
Spores which are present in sporangia are small, a bulb-like structure which is covered by thick walls that protect them until they come in contact with the suitable condition. Under favourable conditions, they germinate and produce new Rhizopus individuals.
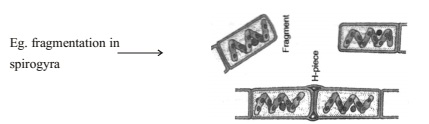
Fragmentation
It takes place in the multicellular organism with simple body organisation. It is the accidental process when the broken pieces of an organism (fragments) grows into a complete organism.
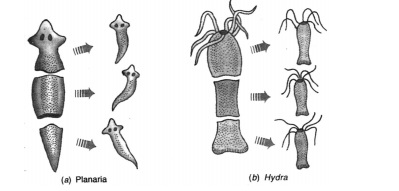
Regeneration
When the simple animals like Hydra, Planaria develop a new individual from their broken older part it is known as regeneration. It is carried out by specialised cells which divide and differentiate to form the complete individual. These cells multiply and from this mass of cells other parts are generated. Regeneration follows an organised sequence referred to as DEVELOPMENT.
Vegetative Propagation
A mode of reproduction in which reproduction takes place from the vegetative parts like the stem, root, leaves.
Methods of Vegetative Propagation
Natural
- By Roots: E.g. adventitious roots of Dahlias
- By Stems: E.g. Potato (tuber), ginger (rhizome)
- By Leaves: E.g. leaves of bryophyllum bear adventitious buds (in the notches of leaf margin) which develop into new plants.
Artificial
- Grafting: E.g. Mango.
- Cutting: E.g. Rose
- Layering: E.g. Jasmine
- Tissue adture: E.g. Orchids, Ornamental Plants.
Benefits of Vegetative Propagation
- Plants can bear flowers, fruits earlier than those produced from seeds.
- Growing plants like Banana, orange, rose, jasmine that have lost the capacity to produce seeds.
- A genetical similarity is maintained in the plants.
- Helps in growing seedless fruits.
- Cheaper and easier method of growing plants.

