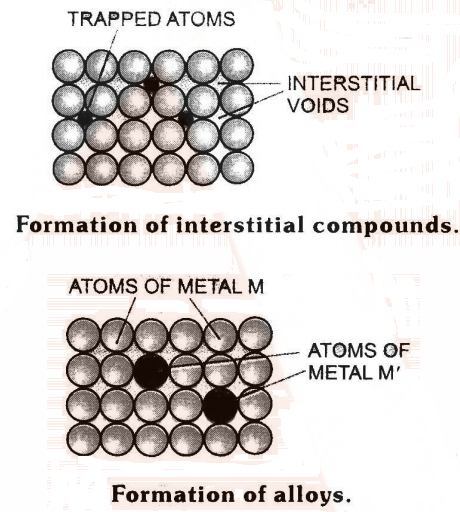
Alloy Formation in d-block elements
- Alloys are homogeneous solid solutions of two or more metals obtained by melting the components and then cooling the melt.
- These are formed by metals whose atomic radii differ by not more than 15% so that the atoms of one metal can easily take up the positions in the crystal lattice of the other (Fig.)
- Now, as transition metals have similar atomic radii and other characteristics, hence they form alloys very readily.
- Alloys are generally harder, have higher melting points and more resistant to corrosion than the individual metals.
- The most commonly used are the ferrous alloys the metals chromium, vanadium, molybdenum, tungsten and manganese are used in the formation of alloy steels and stainless steels.
- Some alloys of transition metals with non-transition metals are also very common. e.g., brass (Cu + Zn) and bronze (Cu + Sn)