
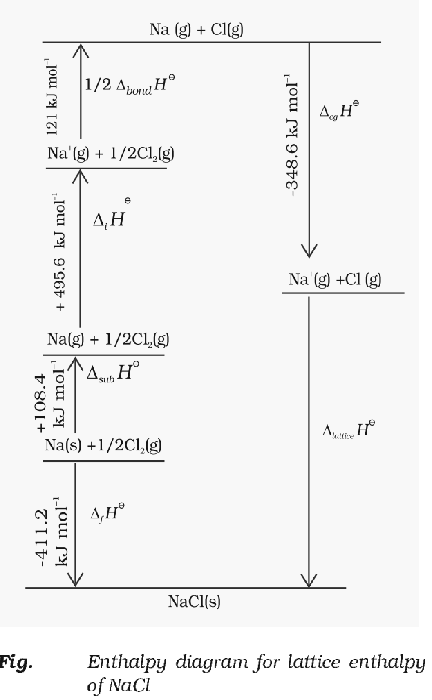
Born-Haber Cycle
The entire thermodynamics process of formation of an ionic crystal lattice is called Born Haber cycle. An ionic compound is formed from its constituents through a series of steps involving conversion of atoms/molecules into gaseous phase for ion formation, ionisation and electron gain to form ions and then the reaction of gaseous ions to form solid lattice.
Spontaneous Process
The physical or chemical process which proceeds by its own in a particular direction under given set of conditions without outside heir is called spontaneous process. It cannot be reversed.
All-natural processes are spontaneous process.
Non-Spontaneous process: They are driven by external work and cannot take place naturally.
Spontaneous Process where no initiation is needed
- Sugar dissolves in water.
- Evaporation of water
- Nitric oxide (NO) reacts with oxygen.
Spontaneous Process where some initiation is required
- Coal keeps on burning once initiated.
- Heating of CaCO3 to give calcium oxide and CO2 is initiated by heat.
![]()
Enthalpy Criterion of Spontaneous Process
All the processes which are accompanied by decrease of energy (exothermic reactions, having negative value of ∆H) occur spontaneously.
It fails when some endothermic reaction occurs spontaneously.
Entropy Criterion of Spontaneous Process
A process is a spontaneous if and only if the entropy of the universe increases.
For a process to be Spontaneous
![]()
At equilibrium state, ∆S = 0,
Limitation of ∆S criterion and need for another term
We cannot find entropy change of surroundings during chemical changes. So, we need another parameter for spontaneity viz Gibbs’ energy of system (G).
Entropy (S)
The entropy is a measure of degree of randomness or disorder of a system. Entropy of a substance is minimum in solid state while it is maximum in gaseous state.
The change in entropy in a spontaneous process is expressed as ∆S
Mathematically,
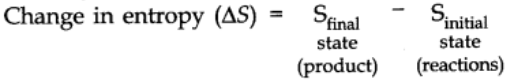
For reversible and isothermal process,
Change in entropy
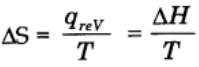
When a system is in equilibrium, ∆S = 0

