
Combustion of Carbon Compounds
- Carbon compounds generally burn (oxidize) in the air to produce carbon dioxide and water, and release heat and light energy.
![]()
- Saturated hydrocarbon burns generally with a blue flame in good supply or air and with a yellow sooty flame in the limited supply of air.
- Sooty flame is seen when unsaturated hydrocarbons are burnt.
- The burning of coal and petroleum emits oxides of sulphur and nitrogen which are responsible for acid rain.
Oxidation of carbon compounds
- Alcohols can be converted to carboxylic acids by oxidizing them using alkaline potassium permanganate or acidified potassium dichromate (they add oxygen to the reactant, thus are called oxidizing agents).
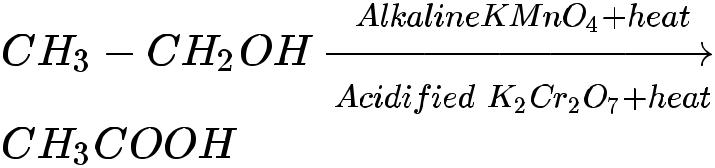
Addiction reaction of carbon compounds
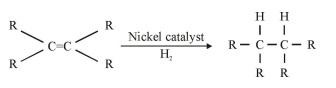 Hydrogen is added to unsaturated hydrocarbon in presence of palladium or nickel as catalyst.
Hydrogen is added to unsaturated hydrocarbon in presence of palladium or nickel as catalyst.
- Saturated fatty acids are harmful for health and oils with unsaturated fatty
- In saturated hydrocarbons, the hydrogen attached to carbon can be replaced by another atom or group of atoms in presence of sunlight.
![]()
![]()
- Consumption of dilute ethanol causes serious health issues and intake of pure alcohol is lethal.

