
Common Ion Effect
If in an aqueous solution of a weak electrolyte, a strong electrolyte is added having an ion common with the weak electrolyte, then the dissociation of the weak electrolyte is decreased or suppressed. The effect by which the dissociation of weak electrolyte is suppressed is known as common ion effect.
For example: In an aqueous solution of CH3COOH, a small amount of CH3COONa (strong electrolyte) has been added.
Due to the presence of common CH3COO– (aq) ions, the equilibrium will be shifted to the left.
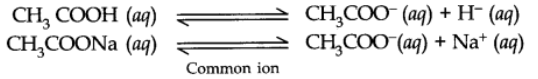
Thus, the dissociation of CH3COOH will get decreased or suppressed.
Hydrolysis of Salts and the pH of their Solutions
Salt Hydrolysis
Salt + water ⇌ Acid + Base
Hydrolysis is a process which is reverse of neutralization reaction.
Hydrolysis of Salts of Strong Acids and Weak Base
e.g., NH4Cl, NH4NO3, etc.
After hydrolysis solution will be acidic pH < 7
Since only cations of the salt participate in the hydrolysis, it is known as cationic hydrolysis.
Hydrolysis of Salts of Strong Base and Weak Acids
Salts in this category are CH3COONa, Na2CO3, Na3PO4, etc.
After hydrolysis solution will be basic pH > 7
In this type of hydrolysis, only anions of salt take part in the hydrolysis, it is known as anionic hydrolysis.
Hydrolysis of Salts of Weak Base and Weak Acids
Salts belong to this type are: CH3COONH4, (NH4)2CO3 etc.
pH of solution depends upon the relative strengths of acid and base.

