
Living organisms respond to various stimuli like heat, light, cold, touch, pressure etc. Example: Withdrawal of hand on touching a hot object.
Control and Coordination in Animals
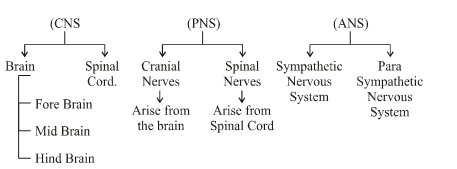
It is brought about in all animals with the help of two main systems
- Nervous System
- Endocrine System
Nervous System:
- Consists of Brain
- Spinal network and
- a huge network of nerves.
Functions of the Nervous system
- To receive the information from the environment
- To receive the information from various body parts. (Stimuli Response)
- To act accordingly through muscles and glands.
Stimulus:
Any change in environment to which the organisms respond is called stimulus.
E.g., touching a hot plate.
Response:
The reaction of our body to a stimulus. E.g. withdrawal of our hand on touching hot plate.
Coordination:
The working together of various organs of the body of an organism in a proper manner to produce an appropriate reaction to a stimulus is called coordination.
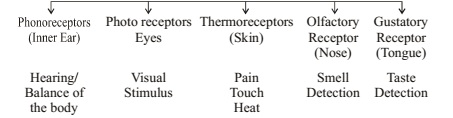
Receptors:
Receptors are specialized tips of some nerve cells that detect the information from the environment.
Neuron:
It is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system.
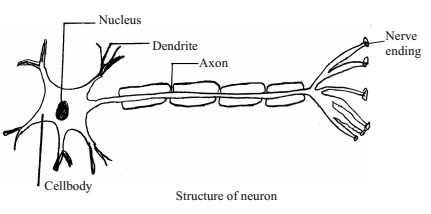
- Neurons (also known as neurones, nerve cells and nerve fibres) are electrically excitable cells in the nervous system that function to process and transmit information. Invertebrate animals, neurons are the core components of the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves.
- The primary components of the neuron are the soma (cell body), the axon (a long slender projection that conducts electrical impulses away from the cell body), dendrites (tree-like structures that receive messages from other neurons), and synapses (specialized junctions between neurons).
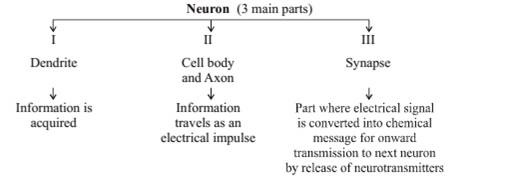
- The axon (nerve fibre) transmits electrical signals from the cell body. The dendrites are branching fibres that receive electrical signals from other neurons. The shape of a neuron is determined by the job it does.
Synapse:
The point of contact between the terminal branches of the axon of one neuron with the dendrite of another neuron is called synapse.
REFLEX ACTION
- Reflex action is an automatic response of the body to a stimulus. e.g. withdrawal of hand, knee-jerk etc. on touching a hot plate.
- Reflex arc: The pathway taken by nerve impulses in a reflex action is called reflex arc.

- Voluntary means it is under the control of a person (e.g. writing)
- Involuntary means it is not under the control of a person. (e.g. heartbeat)
Mechanism of Reflex action:
A reflex mechanism involves a receptor organ, an effector organ, and some type of communication network. When a sensory receptor is stimulated, signals pass from it along with a sensory neuron to the spinal cord. The message travels out of the spinal cord along a motor neuron to the effector organ (e.g., a muscle or a gland), which shows the response. Such a pathway is called a reflex arc. In most cases, however, the basic physiological mechanism behind a reflex is more complicated than the reflex arc theory would suggest. Additional nerve cells capable of communicating with other parts of the body (beyond the receptor and effector) are present in reflex circuits.
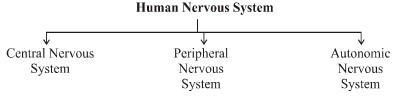
Human Nervous System
The nervous system of vertebrates (including humans is divided into the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The (CNS) is the major division and consists of the brain and the spinal cord. The spinal canal contains the spinal cord, while the cranial cavity contains the brain.
Human Brain
It is enclosed in the cranium (brain box) and is protected by cerebrospinal fluid which acts as a shock absorber. A human brain has three major parts or regions:
- Fore-brain
- Mid Brain
- Hind Brain.
Fore-brain (CEREBRUM)
Most complex/specialized part of the brain is Cerebrum or the forebrain.
Functions of Cerebrum
- Thinking part of the brain
- Control the voluntary actions.
- Store information (Memory)
- Centre associated with HUNGER
- Receives sensory impulses from various body parts and integrates it
Functions of Mid Brain
- It connects the fore-brain with the hind-brain. It is the portion of the central nervous system associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep/wake, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation.
Functions of Hind-Brain

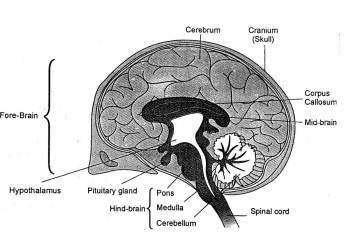
- Brain: The human brain is the command center for the human nervous system. It receives input from the sensory organs and sends output to the muscles.T he human brain has the same basic structure as other mammal brains, but is larger in relation to body size than any other brains
- Brain is protected by a fluid called cerebro-spinal fluid which acts as shock absorber. It has several layers called MENINGES.
- Spinal Cord: Spinal Cord is enclosed in the vertebral column.

