
Extraction of Crude Metal from Concentrated Ore:
The concentrated ore must be converted into a form which is suitable for reduction. Usually the sulphide ore is converted to oxide before reduction. Oxides are easier to reduce. Thus isolation of metals from concentrated ore involves two major steps as given below:
- Conversion to oxide
- Reduction of the oxide to metal.
Conversion to oxide:
Conversion of ore into oxide is carried out in two ways depending upon the nature of ore.
- Calcination: Calcination involves heating when the volatile matter escapes leaving behind the metal oxide:
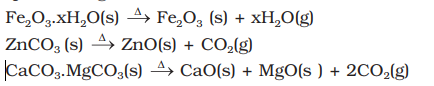
- Roasting: In roasting, the ore is heated in a regular supply of air in a furnace at a temperature below the melting point of the metal point of the metal. Some of the reactions involving sulphide ores are:
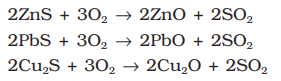
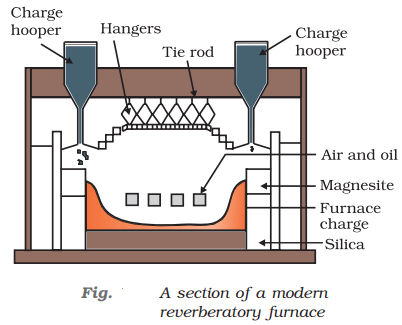
The sulphide ores of copper are heated in the reverberatory furnace. If the ore contains iron, it is mixed with silica before heating. Iron oxide ‘slags of ’* as iron silicate and copper is produced in the form of copper matte which contains Cu2S and FeS.
![]()
Reduction of the oxide to metal:
Reduction of the metal oxide usually involves heating it with some other substance acting as a reducing agent (C or CO or even another metal). The reducing agent (e.g., carbon) combines with the oxygen of the metal oxide.
![]()

