Free Oscillations or Undamped oscillations
If a body, capable of oscillation, is slightly displaced from its position of equilibrium and left to itself, it starts oscillating with a frequency of its own. Such oscillations are called free oscillations. The frequency with which a body oscillates freely is called natural frequency and is given by
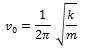
Damped Simple Harmonic Motion
The mechanical energy in a real oscillating system decreases during oscillations because external forces, such as drag, inhibit the oscillations and transfer mechanical energy to thermal energy. The real oscillator and its motion are then said to be damped.
In an oscillatory motion, friction produces three effects:
- It changes the simple harmonic motion into periodic motion.
- It decreases the amplitude of oscillation.
- It slightly reduces the frequency of oscillation.
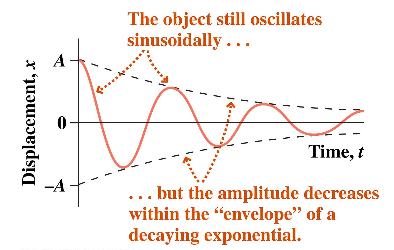
Fig. Damped oscillations
If the damping force is given by
![]()
where v is the velocity of the oscillator and b is a damping constant, then the displacement of the oscillator is given by,
![]()
The amplitude of the damped S.H.M. is
![]()
where a is the amplitude of undamped S.H.M. Clearly, a’ decrease exponentially with time.
The angular frequency of the damped oscillator is
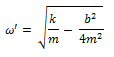
The time period,
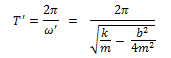
Clearly, damping increases the time period (due to the presence of the term b2/4m2 in the denominator).
The mechanical energy of the damped oscillator at any instant t will be
![]()
Obviously, the total energy decreases exponentially with time.
As damping constant, b= F/v
Therefore, SI unit of
![]()
CGS unit of b = g s-1.

