
Human Eye
The human eye is the optical instrument used which enables us to see. It acts like a camera, enable us to capture the colourful picture of the surroundings. An inverted, real image on light sensitive is formed on the Retina
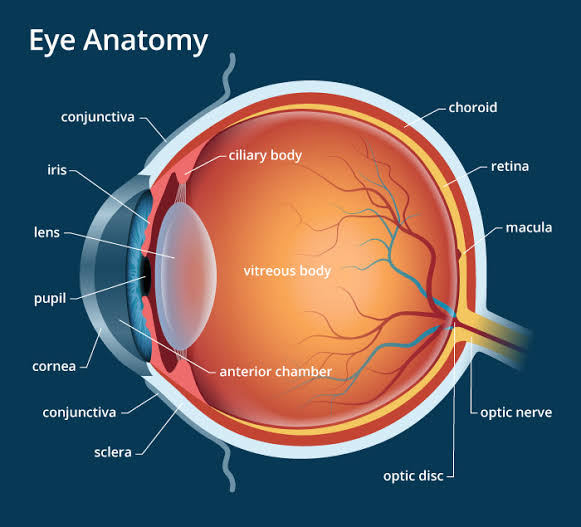
The Various Parts of Eye and their Functions
- Cornea: It is a thin membrane through which light enters. It forms the transparent bulge on the front of the eyeball. Most of the refraction occurs at the outer surface of the cornea.
- Eyeball: it is a convex lens, approximately spherical in shape, with a diameter of about 2.3 cm. It can alter its curvature with help of ciliary muscles.
- Iris: It is a dark muscular diaphragm that controls the size of the pupil. It is behind the cornea. it helps in accommodation of light by changing the size of the pupil.
- Pupil: It regulates and controls the amount of light entering the eye. It is the black opening between aqueous humour & lens. Black in colour. Light entering cannot exit.
- Crystalline eye lens: Provides the focused real & inverted image of the object on the retina. It is composed of a fibrous, jelly-like material. This is a convex lens that converges light at the retina.
- Ciliary muscles: It helps to change the curvature of the eye lens and hence changes its focal length so that we can see the object clearly placed at different positions
- Retina: Thin membrane with large no. of light-sensitive cells.
- There are two types of photoreceptors in the human retina, rods and cones.
- Rods are responsible for vision at low light levels. They do not mediate color vision.
- Cones are active at higher light levels, are capable of color vision.
- When an image is formed at the retina, light-sensitive cells get activated and generate an electrical signal. These signals are sent to the brain via the optic nerve. Brain analyse these signals after which we perceive the object as they are.
- The vitreous body is the clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina of the eyeball of humans and another vertebrate.
- The aqueous humour is a transparent, watery fluid similar to plasma, but containing low protein concentrations.
How does Pupil work?
Example: You would have observed that when you come out of the cinema hall after watching a movie, in the bright sunlight, your eyes get closed. And when you enter the hall from the bright light, you won’t able to see but after some time you would be able to see. Here the pupil of an eye provides a variable aperture, whose size is controlled by the iris
- When the light is bright: Iris contracts the pupil, so that less light enters the eye.
- When the light is dim: Iris expand the pupil, so that more light enters the eye. Pupil opens completely when Iris is relaxed.
Persistence of Vision: It is the time for which the sensation of an object continues in the eye. It is about 1/16th of a second.
Power of Accommodation: The ability of eye lens to adjust its focal length with the help of ciliary muscles is called Power of Accommodation.
Defects of Vision and their Correction
Cataract
The image cannot be seen distinctly because the eye lens becomes milky and cloudy. This condition is known as cataract, it can cause complete or partial loss of vision. This can be corrected by surgical removal of extra growth (cataract surgery).
Myopia (Near Sightedness)
A person can see the nearby object clearly, but cannot see a distant object distinctly.
The image formed in front of the retina.
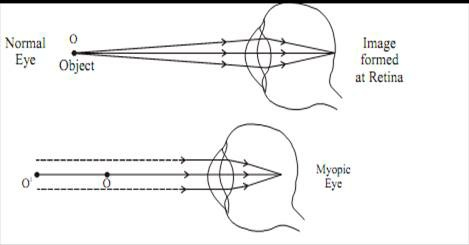
The Reason of defect
- The excessive curvature of eye lens means Eye lens becomes thick and its focal length decreases.
- Elongation of the eyeballll.
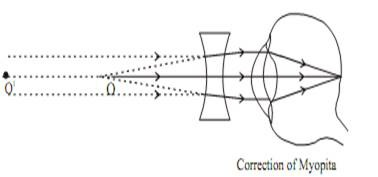
Correction of Myopia
Corrected by using a Concave Lens of appropriate power.
Hypermetropia (Far – Sightedness)
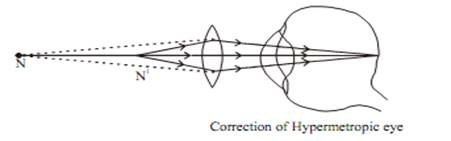
A person cannot see a nearby object clearly, but can see a distant object distinctly.
Image formed at a point behind the retina

The Reason of defect
- Increase in focal length of the eye lens (Thin eye lens)
- Eye ball has become too small.
Correction of Hypermetropia
Corrected by using a Convex Lens of appropriate power.
Presbyopia
As we become old, the power of accommodation of the eye usually decreases, the near point gradually recedes away. This defect is called Presbyopia, a special kind of Hypermetropia. Person may suffer from both myopia and hypermetropia.
Reason of defect
Gradual weakening of ciliary muscles and decreasing the flexibility of the eye lens.
Correction of Presbyopia
Using Bifocal lens with appropriate power.Bifocal lens consist of both concave and convex lens, upper position consist of concave lens and lower portion consist of convex lens.

