
Chemistry is the branch of science that deals with the composition, structure and properties of matter. Chemistry is called the science of atoms and molecule.
Importance of Chemistry
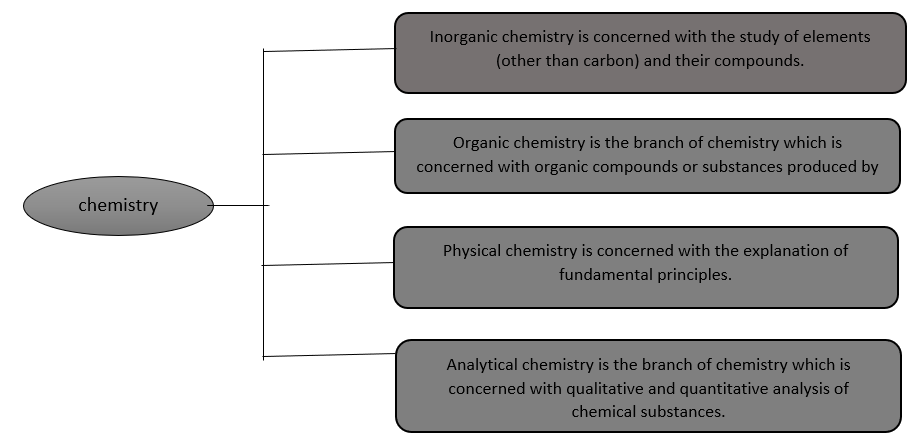
In addition to this biochemistry, war chemistry, nuclear chemistry forensic chemistry, earth chemistry etc., are other branches of chemistry.
Matter
Anything which has mass and occupies space is called matter.
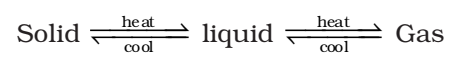
For example, book, pencil, water, air is composed of matter as we know that they have mass and they occupy space.

Properties of Matter and Their Measurement
Every substance has unique or characteristic properties. These properties can be classified into two categories – physical properties and chemical properties.
- Physical Properties: Physical properties are those properties which can be measured or observed without changing the identity or the composition of the substance. Some examples of physical properties are color, odor, melting point, boiling point, density etc.
- Chemical Properties: Chemical properties are those in which a chemical change in the substance occurs. The examples of chemical properties are characteristic reactions of different substances; these include acidity or basicity, combustibility etc.
Chemical Properties
Mixture
A mixture contains two or more substances present in it (in any ratio) which are called its components. A mixture may be homogeneous or heterogeneous.
- Homogeneous mixture- in the homogeneous mixture the components completely mix with each other and its composition is uniform throughout i.e it consists of only one phase. Sugar solution and air are thus, the examples of homogeneous mixtures.
- Heterogeneous mixtures- In a heterogeneous mixture the composition is not uniform throughout and sometimes the different phases can be observed. For example, grains and pulses along with some dirt (often stone) pieces, are heterogeneous mixtures
Pure Substances:
A material containing only one substance is called a pure substance. Pure substances can be further classified into elements and compounds.
- Element- An element is defined as a pure substance that contains only one kind of particles. Depending upon the physical and chemical properties, the elements are further subdivided into three classes, namely: (i) Metals (ii) Non-metals and (iii) Metalloids.
- Compound- A compound is a pure substance containing two or more than two elements combined together in a fixed proportion by mass. Further, the properties of a compound are completely different from those of its constituent elements.
A compound can be further classified into the inorganic and organic compound.
Measurement
Physical quantities: All such quantities which we come across during our scientific studies are called Physical quantities. Evidently, the measurement of any physical quantity consists of two parts:
- The number
- The unit
A unit is defined as the standard of reference chosen to measure any physical quantity.
SI Unit
The International System of Units (in French Le Systeme International d’Unités – abbreviated as SI) was established by the 11th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM from Conference Generale des Poids at Measures).
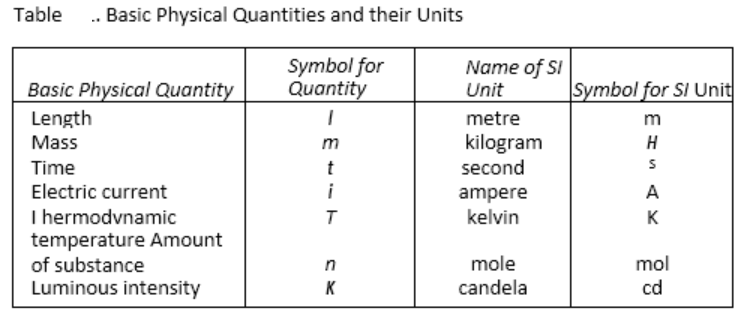
The SI system has seven base units and they are listed in the table given below.
Some Important Definition
Mass:
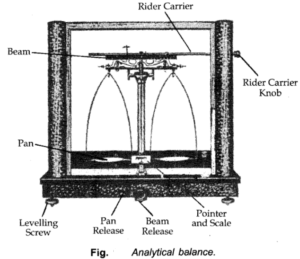
Mass of a substance is the amount of matter present in it. The mass of a substance is constant. The mass of a substance can be determined accurately in the laboratory by using an analytical balance. SI unit of mass is the kilogram.
Weight:
It is the force exerted by gravity on an object. The weight of substance may vary from one place to another due to change in gravity.
Volume:
Volume has the units of (length)3. So, volume has units of m3 or cm3 or dm3. A common unit, litre (L) is not an SI unit, is used for measurement of the volume of liquids. 1L = 1000 mL, 1000 cm3 = 1 dm3.
Density:
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is (the lower case Greek letter rho). SI unit of density is kg m-3.
Temperature:
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. There are three common scales to measure temperature — °C (degree Celsius), °F (degree Fahrenheit) and K (Kelvin). The temperature on two scales is related to each other by the following relationship:
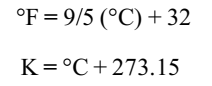
Uncertainty in Measurement
All scientific measurement involves a certain degree of error or uncertainty. The errors which arise depend upon two factors.
- Skill and accuracy of the worker
- Limitations of measuring instruments.
Scientific Notation
In which any number can be represented in the form N x 10n where n is an exponent having positive or negative values and N can vary between 1 to 10).
e.g. we can write 232.508 as 2.32508 x 102 in scientific notation.
Similarly, 0.00016 can be written as 1.6 x 10-4.

