
Metal Carbonyls
The homoleptic complexes in which carbon monoxide (CO) acts as the ligand are called metal carbonyls.
For example: Ni(CO)4
Structure of some important metal carbonyls are:
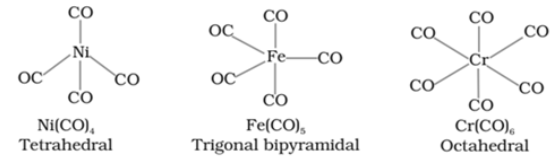
Bonding in metal carbonyls
- The metal-carbon bond in metal carbonyls possess both s and p character. CO as a ligand binds itself to metal atoms through the carbon atom to form the metal-carbon (M-C) bond. It is a weak donor.
- The M–C σ bond is formed by the donation of lone pair of electrons on the carbonyl carbon into a vacant orbital of the metal.
- The M–C π bond is formed by the donation of a pair of electrons from a filled d orbital of metal into the vacant antibonding π* orbital of carbon monoxide. This characteristic property of back bonding which stabilises the metalligand interaction is termed as synergic effect.

Properties of metal carbonyls
- They are generally solids at room temperature and pressure except Ni(CO)4 and Fe (CO)5.
- Mononuclear carbonyls are volatile and toxic.
- Mononuclear carbonyls are either colourless or light coloured.
Stability of Coordination Compounds
The stability of a complex in solution refers to the degree of association between the two-species involved in the state of equilibrium. The magnitude of the (stability or formation) equilibrium constant for the association, quantitatively expresses the stability.

