
A reaction in which oxidation and reduction simultaneously take place is called a redox reaction.
In all redox reaction, the total increase in oxidation number must be equal to the total decrease in oxidation number.
e.g.,
![]()
Types of Redox Reactions
Combination reactions:
A combination reaction may be denoted in the manner:
A + B C
All combustion reactions, which make use of elemental dioxygen, as well as other reactions involving elements other than dioxygen, are redox reactions.
e.g.,
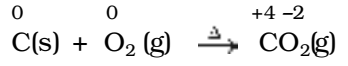
Decomposition reactions:
Decomposition reactions are the opposite of combination reactions. Precisely, a decomposition reaction leads to the breakdown of a compound into two or more components at least one of which must be in the elemental state.
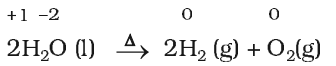
Displacement reactions:
In a displacement reaction, an ion (or an atom) in a compound is replaced by an ion (or an atom) of another element.
X + YZ = XZ + Y
Displacement reactions fit into two categories:
- Metal displacement reactions: A metal in a compound can be displaced by another metal in the uncombined state.
Metal displacement reactions find many applications in metallurgical processes in which pure metals are obtained from their compounds in ores.
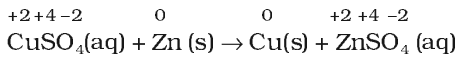
- Non-Metal displacement reactions: The non-metal displacement redox reactions include hydrogen displacement and a rarely occurring reaction involving oxygen displacement.
All alkali metals and some alkaline earth metals (Ca, Sr, and Ba) which are very good reductants, will displace hydrogen from cold water.
![]()
Disproportionation reactions:
A redox reaction in which same element present in a particular compound in a definite oxidation state is oxidized as well as reduced simultaneously is a disproportionation reaction.
Disproportionation reactions are a special type of redox reactions. One of the reactants in a disproportionation reaction always contains an element that can exist in at least three oxidation states. The element in the form of reacting substance is in the intermediate oxidation state and both higher and lower oxidation states of that element are formed in the reaction.
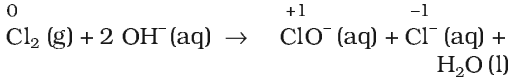
Balancing of Redox Reactions
All balanced equation must satisfy two criteria.
- Atom balance (mass balance): there should be the same number of atoms of each kind on reactant and product side.
- Charge balance: The sum of actual charge on both sides of the equation must be equal. There are two methods for balancing the redox equations.
- Oxidation – number change method
- Ion electron method or half-cell method
Since First method is not very much fruitful for the balancing of redox reactions, students are advised to use second method (Ion electron method) to balance the redox reactions.

