
Ethanoic Acid (Acetic Acid )
- 5-8% solution of acetic acid in water is called vinegar.
- Pure acetic acid is called glacial acetic acid.
| React with | Products |
|---|---|
| Sodium Na | Sodium Ethanoate and hydrogen |
| Sodium carbonate | Sodium Ethanoate, Carbon dioxide and Water |
| Ethanol(in presence of conc sulphuric acid) | Easter and Water |
| Sodium bicarbonate | Sodium Ethanoate, Carbon dioxide and water |
| NaOH | Sodium Ethanoate and Water |
Soaps and Detergents
- Soap is sodium and potassium salt of carboxylic acids with a long chain.
- Soaps are effective with soft water only and ineffective with hard water.
- Detergents are ammonium or sulphonate salts of carboxylic acids with long chain.they are effective with both soft as well as hard water.
- An ionic part (hydrophilic) and a long hydrocarbon chain (hydrophobic)part constitutes the soap molecule.
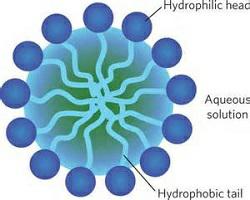
- The long-chain of carboxylic acid, hydrophobic ionic end, hydrophilic Structure of a Soap molecule.
Cleansing Action of Soaps
- Most dirt is oily in nature and the hydrophobic end attaches itself with dirt, while the ionic end is surrounded with molecules of water. This result in the formation of a radial structure called micelles.
- An emulsion is thus formed by soap molecule. The cloth needs to be mechanically agitated to remove the dirt particles from the cloth.
- Scum: The magnesium and calcium salts present in hard water react with soap molecule to form insoluble products called scum, thus obstructing the cleansing action. Use of detergents overcome this problem as the detergent molecule prevents the formation of insoluble product and thus clothes get cleaned.


