
Any substance that has mass and occupies space is called Matter. The matter is composed of atoms or molecules. The force of interaction between atoms/molecules is highest in solids and least in liquids.
Interconversion of States of Matter
These states are interconvertible
- Melting point: This is the temperature at which a matter converts from its solid state to the liquid state. It decreases in the presence of an impurity.
- Boiling point: This is the temperature at which the vapour pressure of a liquid becomes equal to the atmospheric pressure. It increases in the presence of impurity and with rising in pressure. The boiling point of water is 100oC.
- Freezing point: At this temperature, a matter converts from its fluid state into a solid state. The freezing point of water is 0oC.
Evaporation: It is the process of conversion of a liquid into vapours at any temperature.
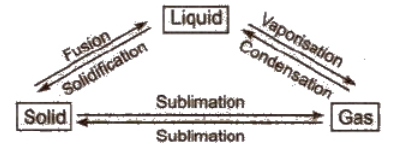
The temperature and pressure at which all the three states of a substance can exist together in equilibrium is called triple point, e.g., ice, liquid water and water vapours can coexist (i.e., ice ↔ water ↔vapour) at 0.0098oC and 4.58 mm.
Factors Deciding Physical State of a Substance
For the gaseous state,
The force of attraction << Thermal energy for the liquid state,
Force of attraction > Thermal energy
For solid state,
Forces of attraction >> Thermal energy

