It is an arrangement of four resistance used to determine one of this resistance quickly and accurately in terms of the remaining three resistances.
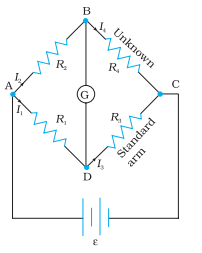
The bridge has four resistors R1, R2, R3 and R4. Across one pair of diagonally opposite points (A and C in the figure) a source is connected. This (i.e., AC) is called the battery arm. Between the other two vertices, B and D, a galvanometer G (which is a device to detect currents) is connected. This line, shown as BD in the figure, is called the galvanometer arm.
![]()
![]()
- When the Wheatstone bridge is balanced, the potential difference between the points B and D is zero.
- The Wheatstone bridge is most sensitive when the resistances in the four arms are of the same order.
- Wheatstone bridge method is not suitable for the measurement of very low and very high resistance.
- If the bridge is balanced, then on interchanging the positions of the galvanometer and the battery there is no effect on the balance of the bridge. That is why the arms BD and Ac are called conjugate arms of the bridge.

