
Evolution
Evolution is the process by which different kinds of living organism are believed to have developed from earlier forms during the history of the earth. Both evolution and classification are interlinked.
- Classification of species is the reflection of their evolutionary relationship.
- The more characteristic two species have in common the more closely they are related.
- The more closely they are related, the more recently they have a common ancestor.
- Similarities among organisms allow us to group them together and to study their characteristic.
Tracing Evolutionary Relationships
Jean Baptiste Lamarck gave the first theory of evolution. The accepted one is The Origin of Species by Charles Darwin. (Evidence of Evolution)
Homologous Organs
Morphological and anatomical evidence. These are the organs that have the same basic structural plan and origin but different functions.
Homologous organs provide evidence for evolution by telling us that they are derived from the same ancestor.
Analogous Organs
These are the organs that have different origin and structural plan but same function example :
Example: Analogous organs provide a mechanism for evolution.
- Fossils: (Paleontological evidence) The remains and relics of dead organisms of the past.
Fossils are preserved traces of living organisms
Fossil Archaeopteryx possesses features of reptiles as well as birds. This suggests that birds have evolved from reptiles.
Examples of Fossils
AMMONITE – Fossil-invertebrate
TRILOBITE – Fossil-invertebrate
KNIGHTIA – Fossil-fish
RAJASAURUS – Fossil dinosaur skull
Age of Fossils

Evolution by Stages
Evolution takes place in stages ie bit by bit over generations.
Fitness Advantage
Evolution of Eyes: Evolution of complex organs is not sudden it occurs due to minor changes in DNA, however, takes place bit by bit over generations.
Functional Advantage Evolutions of Feathers
Feathers provide insulation in cold weather but later they might become useful for flight.
Example: Dinosaurs had feathers, but could not fly using feathers. Birds seem to have later adapted the feathers to fly.
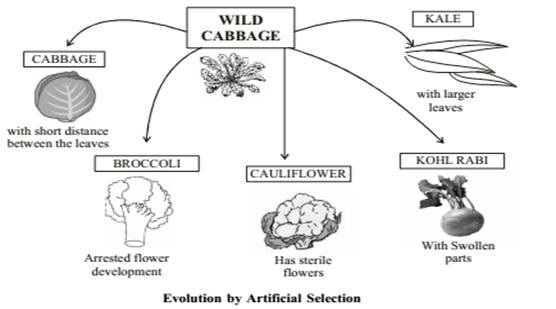
Evolution by Artificial Selection:
Humans have been a powerful agent in modifying wild species to suit their own requirement through out ages by using artificial selection. e.g. (i) From wild cabbage many varieties like broccoli, cauliflower, red cabbage, kale, cabbage and kohlrabi were obtained by artificial selection. (ii) Wheat (many varieties obtained due to artificial selection).
Molecular Phylogeny
- It is based on the idea that changes in DNA during reproduction are the basic events in evolution
- Organisms which are more distantly related will accumulate greater differences in their DNA
Tools to Study Human Evolutionary Relationship
- Excavating
- Time dating
- Fossils
- Determining
- DNA Sequences
Although there is a great diversity of human forms all over the world get all humans are single species


