
Our Environment
Environment means everything which surrounds us. It may include living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components.
- Biotic: Plants and animals.
- Abiotic: Air, water etc.
Environment affect the life and development of an organism in its natural habitat & vice a versa.
- Substances that can be decomposed by the action of micro-organism like bacteria are called bio-degradable. Example of biodegradable wastes: cattle dung, cotton, jute, paper, fruit and vegetable peels, leaves etc.
- Substances which cannot be decomposed by the action of microorganisms are called non-biodegradable. Examples of non-biodegradable wastes: plastics, polythene bags, synthetic fibers, metals, radioactive wastes.
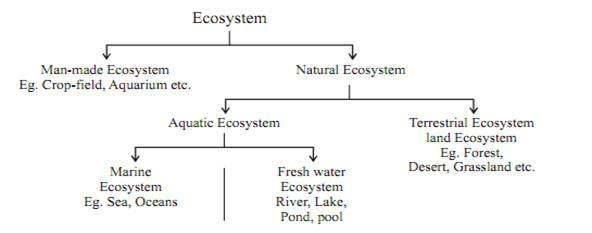
Eco System & Its Components
All the interacting living organisms in an area together with non living components form an ecosystem. So an ecosystem consists of both biotic(living creatures) and abiotic components like temperature, rainfall, wind, soil etc.
 All living organisms are classified on the basis nutrition
All living organisms are classified on the basis nutrition
- Producers: All green plants, blue green algae can produce their food (Sugar & starch) from inorganic substance using light energy (Photosynthesis).
- Consumers: Include organisms which depend on the producers either directly or indirectly for their sustenance. Consumers depend on others for food.
- Decomposers: Fungi & Bacteria which break down (decompose) the dead plant, animal complex compounds into the simpler one. Thus, decomposers help in the replenishment.

