
Isomerism
The phenomenon of existence of two or more compounds possessing the same molecular formula but different properties is known as isomerism.
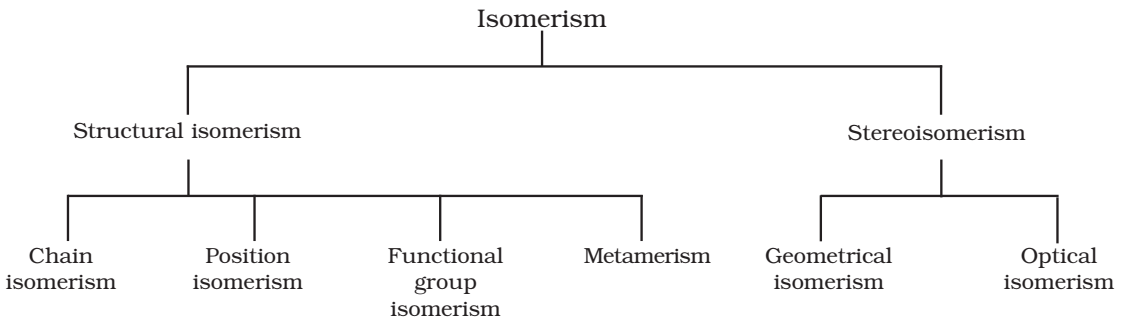
Structural Isomerism:
Compounds having the same molecular formula but different structure.
Chain isomerism:
When two or more compounds have similar molecular formula but different carbon skeletons, these are referred to as chain isomers and the phenomenon is termed as chain isomerism.

Position isomerism:
Compounds which have the same structure of carbon chain but differ in position of double or triple bonds or functional group are called position isomerism.

Functional group isomerism:
Two or more compounds having the same molecular formula but different functional groups are called functional isomers and this phenomenon is termed as functional group isomerism.

Metamerism:
It arises due to different alkyl chains on either side of the functional group in the molecule. For example, C4H10O represents methoxy propane (CH3OC3H7) and ethoxyethane (C2H5OC2H5).
Stereoisomerism
The compounds that have the same constitution and sequence of covalent bonds but differ in relative positions of their atoms or groups in space are called stereoisomers. This special type of isomerism is called as stereoisomerism and can be classified as geometrical and optical isomerism.

