
Sex Determination
Determination of sex of an offspring.
Factors for Sex Determination
Sex Chromosomes
In human beings there are 23 pairs of chromosome. Out of these 22 chromosomes pairs are called autosomes and the last pair of chromosome that help in deciding gender of that individual is called sex chromosome.
– male XY
– female XX

Evolution
Evolution is the sequence of gradual changes which takes place in the primitive organisms, over millions of years, in which new species are produced.
Situation – I
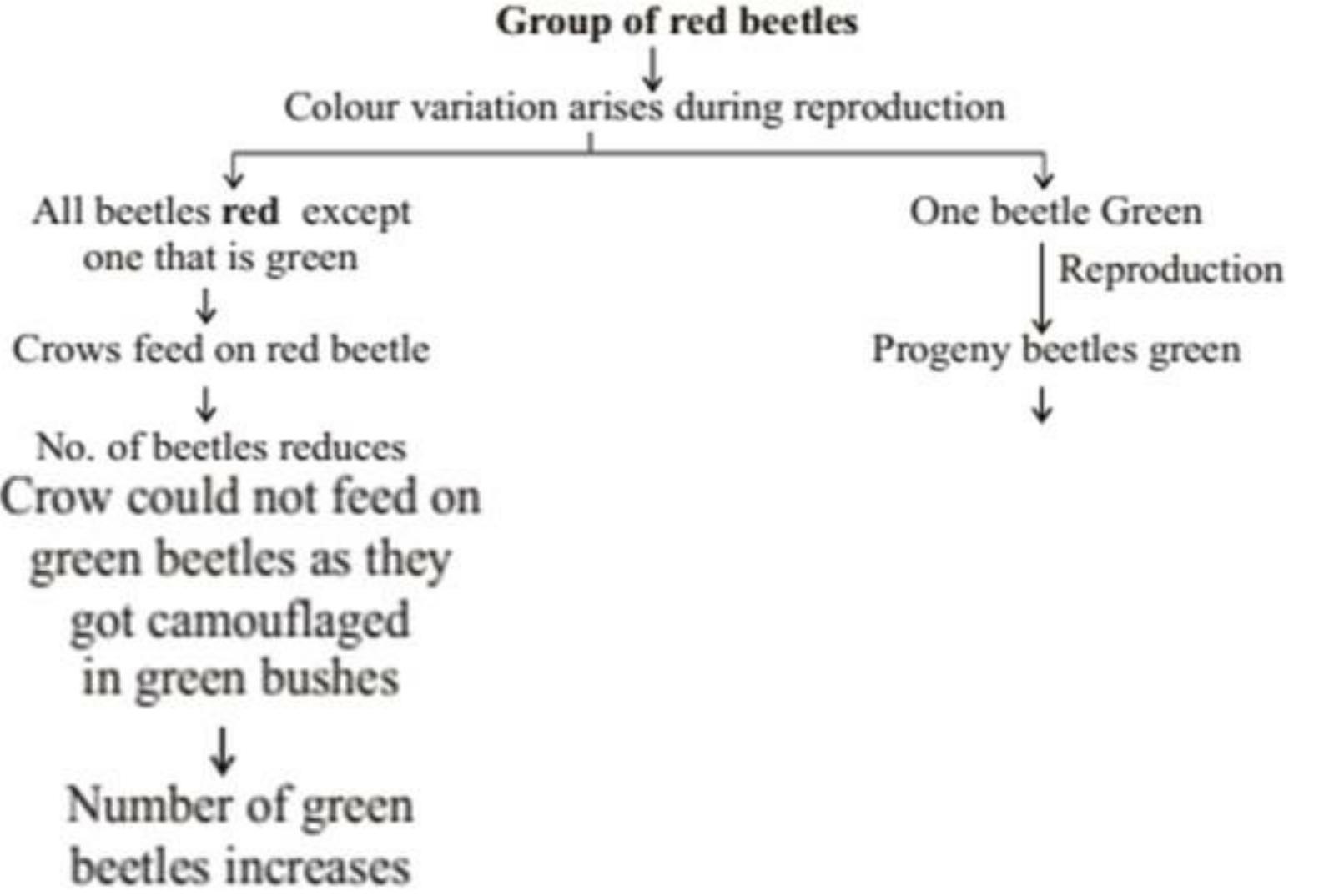
- Green beetles got the survival advantage or they were naturally selected as they were not visible in green bushes. This natural selection is exerted by crows resulting in adaptations in the beetles to fit better in their environment
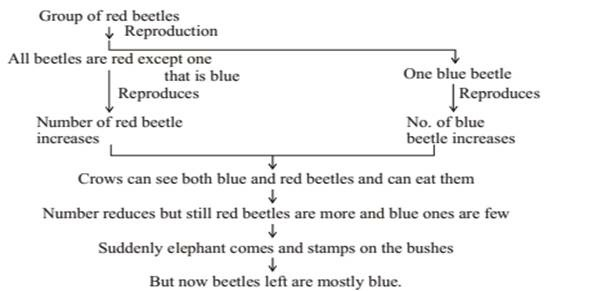
Situation-II
- Blue beetles did not get survivals advantage. Elephant suddenly caused major havoc in beetle population otherwise their number would have been considerably large.
- From this we can conclude that accidents can change the frequency of some genes even if they do not get survival advantage: This is called genetic drift and it leads to variation.
Situation III :
No genetic change has occurred in the population of beetle.The population gets affected for a short duration only due to environmental changes.
Speciation
Micro Evolution:
It is the evolution which is on a small scale. e.g. change in body colour of beetles.
The process by which new species develop from the existing species is known as speciation.
Speciation:
it is the process of formation of new species.
Species:
A group of similar individuals within a population that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring. Factors which lead to speciation: Geographical isolation, genetic drifts and variations.
Geneflow:
It is an exchange of genetic material by interbreeding between populations of same species or individuals
Ways by which speciation takes place
Speciation takes place when the variation is combined with geographical isolation.
Gene flow: occurs between the population that is partly but not completely separated.
 Genetic Drift
Genetic Drift
It is the random change in the frequency of alleles (gene pair) in a population over successive generations.
Natural Selection: The process by which nature selects and consolidate those organisms which are more suitably adapted and possesses favourable variations
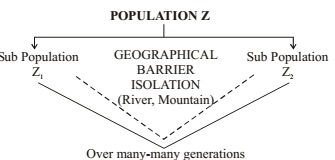
Genetic drift takes place due to :
- Severe changes in the DNA
- Change in the number of chromosomes

