
A balanced chemical equation together with the value of ∆rH and the physical state of reactants and products is known as thermochemical equation.

Conventions regarding thermochemical equations
- The coefficients in a balanced thermochemical equation refer to the number of moles of reactants and products involved in the reaction.
- The numerical value of ∆rH⊖ refers to the number of moles of substance specified by an equation.
- If a chemical reaction is reversed, the value of ∆rH⊖ is reversed in sign.
For example:
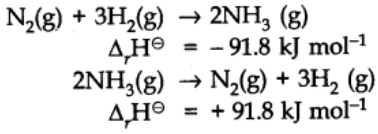
Hess’s Law of Constant Heat Summation
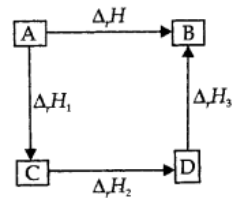
If a reaction takes place in several steps then its standard reaction enthalpy is the sum of the standard enthalpies of the intermediate reactions into which the overall reaction may be divided at the same temperature. This is called the Hess Law.
Let us consider the following reactions:

On combining the two reactions,

In general, it can be represented as,
![]()
Applications of Hess’s law are:
- In determination of beat of formation.
- In determination of heat of transition.
- In determination of heat of hydration.
- To calculate bond energies.

