
Atomic Number and Mass Number
Atomic Number (Z):
The number of protons present in the nucleus is equal to the atomic number (Moseley 1913).
Atomic Number (Z)= Number of protons in the nucleus of an atom = Number of electrons in a neutral atom
Example:
- The number of protons in the hydrogen nucleus is 1, in sodium atom, it is 11, therefore, their atomic number are 1 and 11.
- In order to keep the electrical neutrality, the number of electrons in an atom is equal to the number of protons (atomic number, Z).
- For example, the number of electrons in a hydrogen atom and sodium atom are 1 and 11 respectively.
Mass Number (A):
Sum of the number of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus.
Mass Number (A) = Number of protons (p) + Number of neutrons (n).
Isotopes
Atoms with an identical atomic number but a different atomic mass number are known as Isotopes.
Isotopes of Hydrogen:
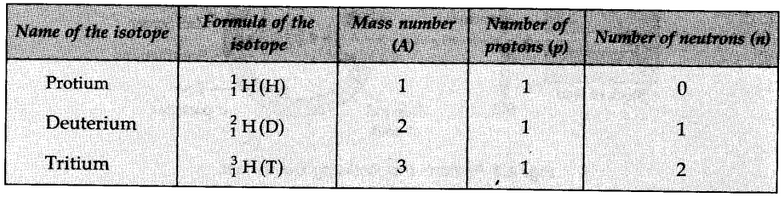
These three isotopes as shown in the figure below:
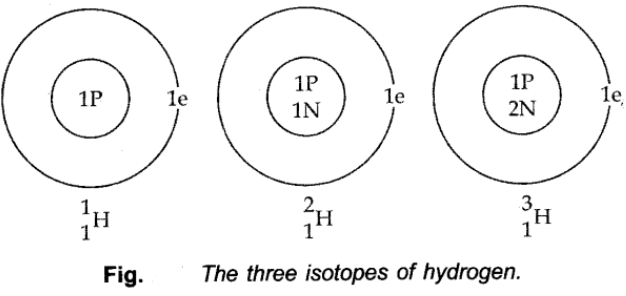
Isotopes of Chlorine:
These are two isotopes of chlorine with mass number 35 and 37.
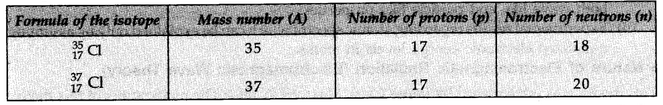
The two isotopes differ in their number of neutrons, having 18 and 20 neutrons, respectively.
Isobars
- Isobars are the atoms with the same mass number but the different atomic number.
For example,
![]()
- Each of these has the same mass number but a different atomic number.

