
Dobereiner’s Triads (1829)
Dobereiner classified the elements into groups of three elements with similar properties in such a manner so that the atomic weight of the middle element was the arithmetic mean of the order two, e.g.,

Limitations of Dobereiner’s Triads
The triads given by Dobereiner were helpful in grouping some elements with similar characteristics together, but he could not arrange all the elements known at that time into triads.
Newland’s Octaves (1864) (Law of Octaves)
Newland states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic masses, every eighth element has properties similar to the first just like in the musical not (Every eighth musical not 1S the same as the first-mentioned note). This can be illustrated as given below:

Limitation of Newland’s Law of Octaves
- This classification was successful up to the element calcium.
- When noble gas elements were discovered at a later stage, their inclusion in these octaves disturbed the entire arrangement.
Lother Meyer’s Atomic Volume Curve (1869)
Meyer presented the classification of elements in the form of a curve between atomic volume and atomic masses and state that the properties of the elements are the periodic function of their atomic volumes.
Here,
atomic volume = molecular mass / density
He concludes that the elements with similar properties occupy a similar position in the curve.
Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
Mendeleev’s Periodic Table is based upon Mendeleev’s periodic law which states “The physical and chemical properties of the elements are a periodic function of their atomic masses.”
At the time of Mendeleev, only 63 elements were known.
This Periodic Table is divided into seven horizontal rows (periods) and eight vertical columns (groups). Zero group was added later on in the modified Mendeleev’s Periodic table.
Importance of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
Few important achievements of the Periodic Table are
- A systematic study of the elements.
- Prediction of new elements and their properties. He left space for the elements yet to be discovered. E.g., he left spaces for Ga and Ge and named these elements as Era-aluminium (Ga) and EKa-silicon (Ge) respectively.
- Atomic mass correction of doubtful elements on the basis of their expected positions and properties.
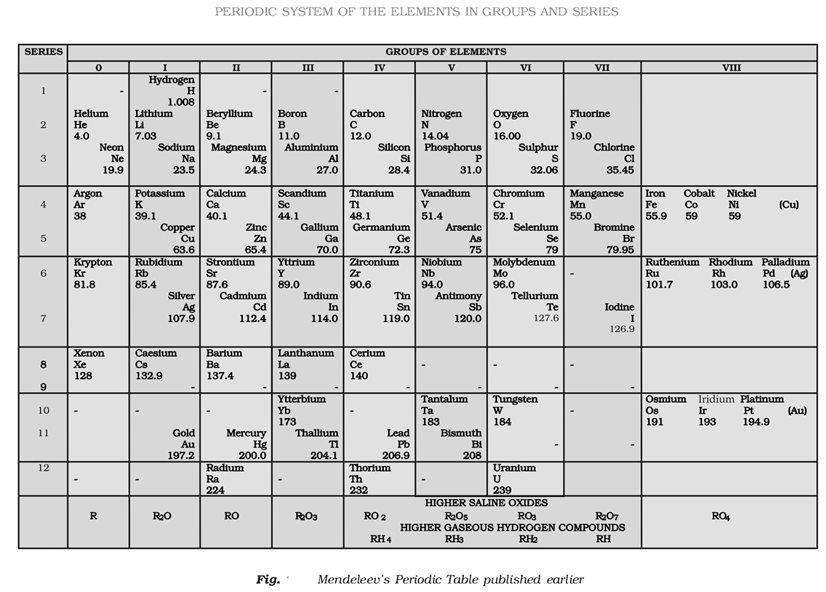
Defects in the Mendeleev’s Periodic table
- Hydrogen has been placed in group IA (alkali metals). But it also resembles with halogens of group VI1A. Thus, its position in the Mendeleev’s Periodic Table is controversial.
- The position of isotopes: As Mendeleev’s classification is based on atomic weight, Isotopes would have to be placed in different positions due to their different atomic weights, e.g.
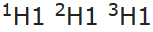 would occupy different positions.
would occupy different positions. - Anomalous positions of some elements: Without any proper justification, in some case, the elements with higher atomic mass precedes the elements with lower atomic mass.
For example, AI (atomic weight = 39.9) precedes K (atomic weight = 39.1)
- The position of Lanthanoids and actinoids: Lanthanoids and actinoids were not placed in the main Periodic table.

