
Sodium Hydroxides (Caustic Soda), NaOH:
Preparation:
Electrolysis of Brine:
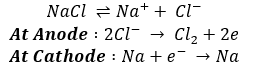
Caustication of Na2CO3 (Gossage’s method):
![]()
Since the Ksp(CaCO3) < Ksp(Ca(OH)2), the reaction shifts towards right.
Properties:
- It is white crystalline, deliquescent, highly corrosive solid.
- It is stable towards heat.
- Its aqueous solution is alkaline in nature and soapy in touch.
- Acidic and amphoteric oxides get dissolved easily. E.g.,
![]()
Sodium Carbonate (Washing Soda) Na2CO3 .10H2O
Preparation:
Leblanc Process:
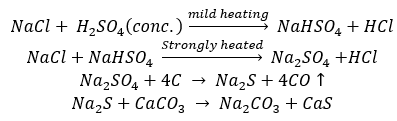
Solvay Process:
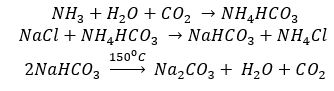
Properties:
- Anhydrous Na2CO3 is called as soda ash, which does not decompose on heating but melts at 852oC.
- It forms number of hydrates.
- Hydrated Na2CO3 is called washing soda (Na2CO3.10H2O) and is prepared by Le Blanc process solvay process and electrolytic process.
Uses:
It is widely used in glass making as smelter.
Sodium Chloride
Prepared from brine containing 25% NaCl.
Properties:
- It is non-hygroscopic but the presence of MgCl2 in common salt renders it hygroscopic.
- It is used to prepare freezing mixture in laboratory [Ice-common salt mixture is called freezing mixture and temperature goes down to -23oC.]
- For melting ice and snow on road.
Sodium Hydrogen carbonate (Baking Soda), NaHCO3
Sodium hydrogen carbonate is known as baking soda because it decomposes on heating to generate bubbles of carbon dioxide (leaving holes in cakes or pastries and making them light and fluffy).
Sodium hydrogen carbonate is made by saturating a solution of sodium carbonate with carbon dioxide. The white crystalline powder of sodium hydrogen carbonate, being less soluble, gets separated out.
![]()
Sodium hydrogen carbonate is a mild antiseptic for skin infections. It is used in fire extinguishers.
Calcium Carbonate
It occurs in nature as marble, limestone, chalk, calcite etc. It is prepared by dissolving marble or limestone in HCl and removing iron and aluminum present, by precipitating with NH3 and then adding (NH4)2 CO3 to the solution.
![]()
Properties:
- It is dissociates above 1000oC as follows:
![]()
- It dissolves in water containing CO2 forming Ca (HCO3)2 but is precipitated from the solution by boiling.
![]()
Calcium Oxide or Quick Lime (CaO):
It is commonly called as quick lime or lime and made by decomposing lime stone at a high temperature about 1000oC.
![]()
Properties:
- It is white amorphous powder of m.p. 2570oC.
- It emits intense light (lime light), when heated in oxygen-hydrogen flame.
- It is a basic oxide and combines with some acidic oxide. e.g.,
![]()
- It combines with water to produce slaked lime.
![]()

