- Unsaturated hydrocarbon which have triple bond.
- General molecular formular CnH2n-2
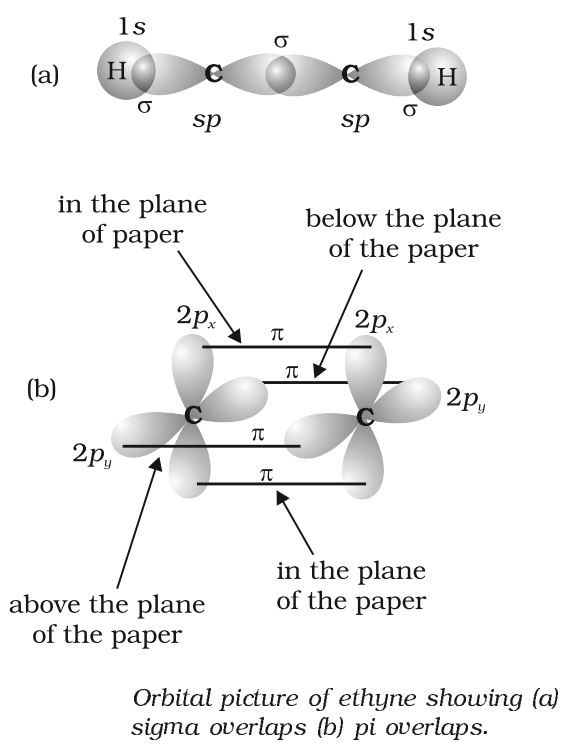
- sp hybridization
- Shown chain, positional and functional isomerism
Nomenclature of alkynes
IUPAC System: The IUPAC names of alkynes are obtained by dropping the ending-ane of the parent alkane and adding the suffix-yne. Carbon chain including the triple bond is – numbered from the end nearest this bond. The position of the triple bond is indicated by prefixing the number of carbon preceding it to the name of the alkyne.
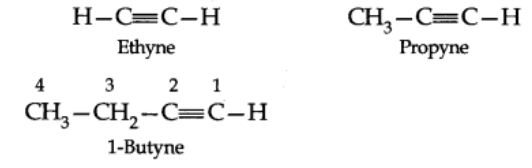
Structure of triple bond (Ethyne)
Preparation of Alkynes
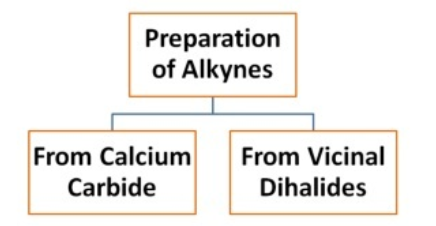
Preparation of Alkynes from calcium carbide
- First calcium carbide is prepared by heating quick lime with coke.
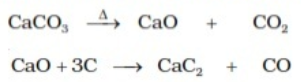
- Then treat calcium carbide with water.
![]()
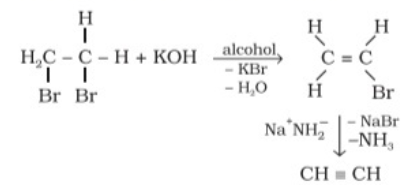
Preparation of Alkynes from vicinal dihalides
- On treating vicinal dihalides with alcoholic potassium hydroxide dehydrohalogenation occurs.
- One molecule of hydrogen halide is eliminated to form alkenyl halide which on treatment with sodamide gives alkyne.
Physical properties of Alkynes
- It follows the same trend of alkenes and alkanes.
- First three members of alkenes are gases, the next eight (C5 – C12) are liquids and the higher ones are solids.
- They are colourless.
- Except Ethyene all other members of alkenes are odourless.
- They are weakly polar in nature.
- They are insoluble with water but soluble in organic solvents like ethers, carbon tetrachloride and benzene.
- With increase in molar mass their melting point, boiling point and density also increase.
Chemical properties of Alkyne

Acidic character of alkyne
These reactions are not shown by alkenes, alkanes and non-terminal alkynes, hence used for distinction between alkane, alkene and alkyne.
Acetylenic hydrogens are acidic in nature due to 50% a-character in sp-hybridised orbitals.
Acidity of alkynes is lesser than water.
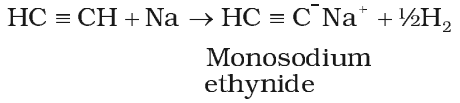
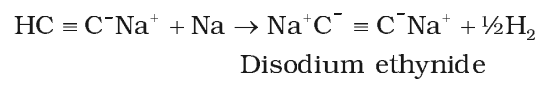

Acidic behavior order

Electrophillic addition reactions
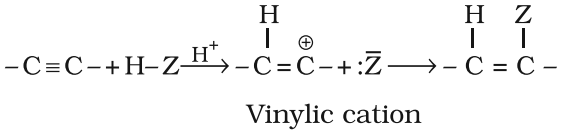
The addition product formed depends upon the stability of vinylic carbon. Addition on unsymmetrical alkynes takes place according to Markovnikov’s rule.
Addition of dihydrogen
![]()
Addition of halogens
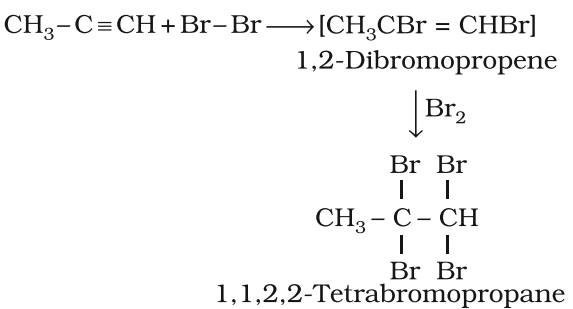
Addition of hydrogen halides
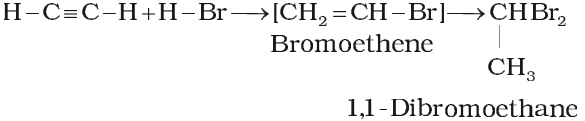
Addition of water (Hydration):
Acid catalyzed addition of water.

Polymerisation
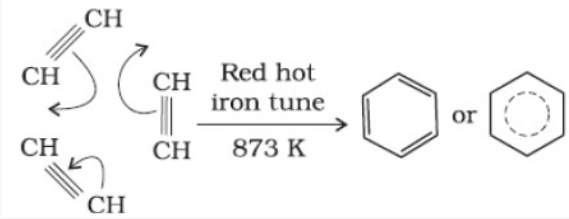
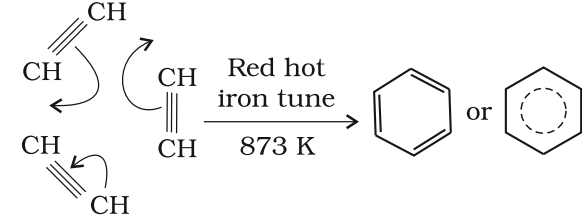
Cyclic polymerisation:
Ethyne on passing through red hot iron tube at 873K undergoes cyclic polymerization. Three molecules polymerise to form benzene, which is the starting molecule for the preparation of derivatives of benzene, dyes, drugs and large number of other organic compounds.
Linear Polymerisation:
Liner Polymersation of ethyne gives polyacetylene or polyethyne which is a high molecular weight polyene containing repeating units of (CH = CH – CH = CH) and can be represented as — (CH = CH – CH = CH)n — b. Cyclic polymerization- results in the formation of aromatic compound.